Diprotin A
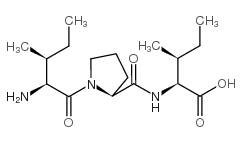
Diprotin A structure
|
Common Name | Diprotin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90614-48-5 | Molecular Weight | 341.44600 | |
| Density | 1.14 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 583.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H31N3O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 306.5ºC | |
|
In vitro assessment of the multifunctional bioactive potential of Alaska pollock skin collagen following simulated gastrointestinal digestion.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(7) , 1514-20, (2015) Dietary mineral deficiency, hypertension and diabetes have become serious human health problems. Dietary approaches are increasingly being investigated to address these issues. Identification of food-derived biological peptides has become an important approac... |
|
|
Antidiabetic property of Symplocos cochinchinensis is mediated by inhibition of alpha glucosidase and enhanced insulin sensitivity.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e105829, (2014) The study is designed to find out the biochemical basis of antidiabetic property of Symplocos cochinchinensis (SC), the main ingredient of 'Nisakathakadi' an Ayurvedic decoction for diabetes. Since diabetes is a multifactorial disease, ethanolic extract of th... |
|
|
Utilisation of the isobole methodology to study dietary peptide-drug and peptide-peptide interactive effects on dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibition.
Food Funct. 6(1) , 313-20, (2015) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) is used as a means to regulate post-prandial serum glucose in type 2 diabetics. The effect of drug (Sitagliptin®)/peptide and binary peptide mixtures on DPP-IV inhibition was studied using an isobole approach. Fi... |
|
|
Total body irradiation is permissive for mesenchymal stem cell-mediated new bone formation following local transplantation.
Tissue Eng. Part A 20(23-24) , 3212-27, (2014) Skeletal injury is a major clinical challenge accentuated by the decrease of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (BMSCs) with age or disease. Numerous experimental and clinical studies have revealed that BMSCs hold great promise for regenerativ... |
|
|
Effects of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide in juvenile transgenic pigs modeling a pre-diabetic condition.
J. Transl. Med. 13 , 73, (2015) The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) agonist liraglutide improves glycemic control and reduces body weight of adult type 2 diabetic patients. However, efficacy and safety of liraglutide in adolescents has not been systematically investigated. Furtherm... |
|
|
A thin-layer chromatography-bioautographic method for detecting dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in plants.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1411 , 116-22, (2015) A thin-layer chromatography (TLC)-bioautographic method was developed with the aim to detect dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) inhibitors from plant extracts. The basic principle of the method is that the enzyme (DPP IV) hydrolyzes substrate (Gly-Pro-p-nitroan... |
|
|
Degradation and Stabilization of Peptide Hormones in Human Blood Specimens.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0134427, (2015) Plasma hormone peptides, including GLP-1, GIP, Glucagon, and OXM, possess multiple physiological roles and potential therapeutic and diagnostic utility as biomarkers in the research of metabolic disorders. These peptides are subject to proteolytic degradation... |
|
|
Lipid-induced peroxidation in the intestine is involved in glucose homeostasis imbalance in mice.
PLoS ONE 6(6) , e21184, (2011) Daily variations in lipid concentrations in both gut lumen and blood are detected by specific sensors located in the gastrointestinal tract and in specialized central areas. Deregulation of the lipid sensors could be partly involved in the dysfunction of gluc... |
|
|
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a potential target for selective prodrug activation and chemotherapeutic action in cancers.
Mol. Pharm. 11(12) , 4385-94, (2014) The efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs is often offset by severe side effects attributable to poor selectivity and toxicity to normal cells. Recently, the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) was considered as a potential target for the delivery of chemothe... |
|
|
Dose-dependent effects of a soluble dietary fibre (pectin) on food intake, adiposity, gut hypertrophy and gut satiety hormone secretion in rats.
PLoS ONE 10(1) , e0115438, (2015) Soluble fermentable dietary fibre elicits gut adaptations, increases satiety and potentially offers a natural sustainable means of body weight regulation. Here we aimed to quantify physiological responses to graded intakes of a specific dietary fibre (pectin)... |