| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
3-(1-Naphthyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazol-3-ium
CAS:1719-71-7 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
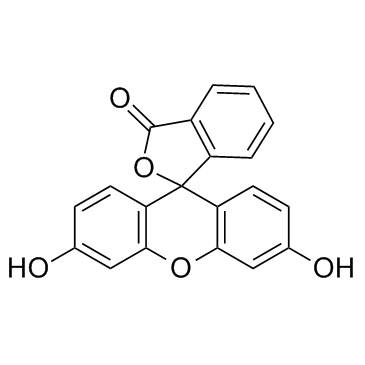 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
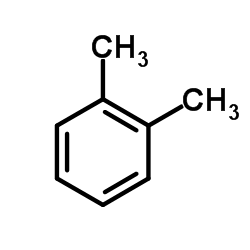 |
o-xylene
CAS:95-47-6 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
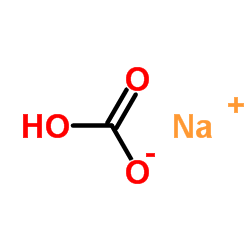 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
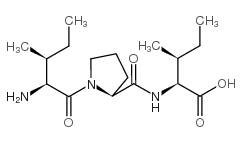 |
Diprotin A
CAS:90614-48-5 |