TRAM-34
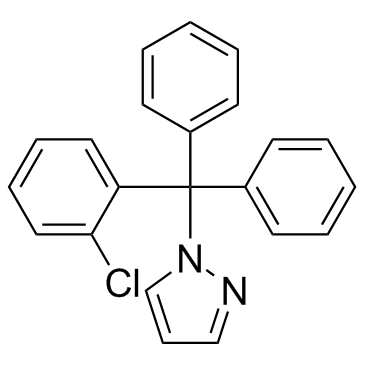
TRAM-34 structure
|
Common Name | TRAM-34 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 289905-88-0 | Molecular Weight | 344.837 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 510.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H17ClN2 | Melting Point | 145-147ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 262.4±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Kv1.3 lymphocyte potassium channel inhibition as a potential novel therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke.
CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 13(5) , 801-6, (2014) Stroke-induced immunosuppression (SIIS) leads to severe complications in stroke patients, including an increased risk of infections. However, functional alterations of T lymphocytes during SIIS are poorly described in acute ischemic stroke (AIS). We aimed to ... |
|
|
Eugenol dilates mesenteric arteries and reduces systemic BP by activating endothelial cell TRPV4 channels.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 , 3484-94, (2015) Eugenol, a vanilloid molecule found in some dietary plants, relaxes vasculature in part via an endothelium-dependent process; however, the mechanisms involved are unclear. Here, we investigated the endothelial cell-mediated mechanism by which eugenol modulate... |
|
|
Impairment of IKCa channels contributes to uteroplacental endothelial dysfunction in rat diabetic pregnancy.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 309 , H592-604, (2015) Diabetes in rat pregnancy is associated with impaired vasodilation of the maternal uteroplacental vasculature. In the present study, we explored the role of endothelial cell (EC) Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels of small conductance (SKCa channels) and intermed... |
|
|
5-hydroxytryptamine has an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-like effect on coronary flow in isolated rat hearts.
J. Biomed. Sci. 22 , 42, (2015) 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)-induced coronary artery responses have both vasoconstriction and vasorelaxation components. The vasoconstrictive effects of 5-HT have been well studied while the mechanism(s) of how 5-HT causes relaxation of coronary arteries has be... |
|
|
Pannexin 1 facilitates arterial relaxation via an endothelium-derived hyperpolarization mechanism
FEBS Lett. 589(10) , 1164-70, (2015) • We studied endothelium-dependent relaxations in control (WT) and Panx1−/− (KO) mice. • The EDH-like component of endothelium-dependent relaxation is impaired in KO mice. • Blockade of purinergic signaling reduces EDH-like component in WT, but not in KO mice... |
|
|
Piezo1 links mechanical forces to red blood cell volume.
Elife 4 , (2015) Red blood cells (RBCs) experience significant mechanical forces while recirculating, but the consequences of these forces are not fully understood. Recent work has shown that gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated Piezo1 cation channels are asso... |
|
|
Upregulation of KCa3.1 K(+) channel in mesenteric lymph node CD4(+) T lymphocytes from a mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced inflammatory bowel disease.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 306(10) , G873-85, (2014) The intermediate-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel KCa3.1/KCNN4 plays an important role in the modulation of Ca(2+) signaling through the control of the membrane potential in T lymphocytes. Here, we study the involvement of KCa3.1 in the enlargement o... |
|
|
Cinnamaldehyde and cinnamaldehyde-containing micelles induce relaxation of isolated porcine coronary arteries: role of nitric oxide and calcium.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 9 , 2557-66, (2014) Cinnamaldehyde, a major component of cinnamon, induces the generation of reactive oxygen species and exerts vasodilator and anticancer effects, but its short half-life limits its clinical use. The present experiments were designed to compare the acute relaxin... |
|
|
Diminished neurogenic femoral artery vasoconstrictor response in a Zucker obese rat model: differential regulation of NOS and COX derivatives.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e106372, (2014) Peripheral arterial disease is one of the macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study addresses femoral artery regulation in a prediabetic model of obese Zucker rats (OZR) by examining cross-talk between endothelial and neural factors.... |
|
|
Nobiletin Stimulates Chloride Secretion in Human Bronchial Epithelia via a cAMP/PKA-Dependent Pathway.
Cell Physiol. Biochem. 37 , 306-20, (2015) Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid isolated from tangerines, alters ion transport functions in intestinal epithelia, and has antagonistic effects on eosinophilic airway inflammation of asthmatic rats. The present study examined the effects of nobiletin on basal sh... |