(Z)-β-ocimene
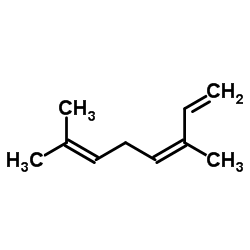
(Z)-β-ocimene structure
|
Common Name | (Z)-β-ocimene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13877-91-3 | Molecular Weight | 136.234 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 175.2±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16 | Melting Point | -27.17°C (estimate) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 46.9±13.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS02 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Determination of the chemical composition and in vitro antioxidant activities of essential oil and methanol extracts of Echinophora platyloba DC.
Nat. Prod. Res. 25(17) , 1585-95, (2011) This study was designed to examine the chemical composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of essential oil and methanol extracts of Echinophora platyloba from Iran. Gas chromatography (GC) and GC/MS (mass spectrometry; MS) analysis of the essential oil re... |
|
|
Evaluation of essential oils for maintaining postharvest quality of Thompson seedless table grape.
Nat. Prod. Res. 26(1) , 77-83, (2012) The effects of postharvest spraying of essential oils from sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum), fennel (Foeniculum vulgare), summer savory (Satureja hortensis) and thyme (Thymus vulgaris) on fungal decay and quality parameters of the 'Thompson seedless' table grap... |
|
|
Volatile organic components of fresh leaves as indicators of indigenous and cultivated citrus species in Taiwan.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 74(4) , 806-11, (2010) The volatile components of fresh leaves from 15 citrus species were investigated by headspace SPME with a GC-MS analysis. Three indigenous Taiwan citrus species, Citrus taiwanica, C. tachibana and C. depressa, were the major subjects. Eighty volatile organic ... |
|
|
Chemical composition and anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity of essential oils obtained from leaves of Xylopia frutescens and X. laevigata (Annonaceae).
Nat. Prod. Commun. 8(3) , 403-6, (2013) Essential oils from leaves of Xylopia frutescens (XFMJ) and two specimens of Xylopia laevigata (XLMC and XLSI) were obtained by hydrodistillation using a Clevenger-type apparatus, and analyzed by GC-MS and GC-FID. Sesquiterpenes dominated the essential oils. ... |
|
|
Volatiles from apple trees infested with light brown apple moth larvae attract the parasitoid Dolichogenidia tasmanica.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(38) , 9562-6, (2012) The volatile compounds emitted from uninfested apple seedlings, cv. Royal Gala, and apple seedlings infested with generalist herbivore Epiphyas postvittana larvae were sampled using headspace collection and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Ni... |
|
|
Role of pathogen-induced volatiles in the Nicotiana tabacum-Golovinomyces cichoracearum interaction.
Plant Physiol. Biochem. 52 , 9-20, (2012) Plant injuries activate signal transduction cascades mediated by the plant hormones, which lead to enhanced expression of defence related genes and/or to changes in the emission of volatile organic compounds that can act as semiochemicals. In this research we... |
|
|
Comparative analysis of the oil and supercritical CO2 extract of Ridolfia segetum (L.) Moris.
Nat. Prod. Res. 21(5) , 412-7, (2007) Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction allowed to obtain the volatile oil of different aerial parts of Ridolfia segetum (L.) Moris. Extraction conditions were as follows: pressure, 90 bar; temperature, 50 degrees C and carbon dioxide flow, Phi = 1.0 kg h(-1)... |
|
|
Effects of feeding Spodoptera littoralis on lima bean leaves: IV. Diurnal and nocturnal damage differentially initiate plant volatile emission.
Plant Physiol. 146(3) , 965-73, (2008) Continuous mechanical damage initiates the rhythmic emission of volatiles in lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus) leaves; the emission resembles that induced by herbivore damage. The effect of diurnal versus nocturnal damage on the initiation of plant defense respon... |
|
|
Rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of OH and O3 with β-ocimene, β-myrcene, and α- and β-farnesene as a function of temperature.
J. Phys. Chem. A 115(4) , 500-6, (2011) The rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of hydroxyl radicals and ozone with the biogenic hydrocarbons β-ocimene, β-myrcene, and α- and β-farnesene were measured using the relative rate technique over the temperature ranges 313-423 (for OH) and 298-318 ... |
|
|
Associative learning of plant odorants activating the same or different receptor neurones in the moth Heliothis virescens.
J. Exp. Biol. 208(Pt 4) , 787-96, (2005) The importance of olfactory learning in host plant selection is well demonstrated in insects, including the heliothine moths. In the present study olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension response was performed to determine the moths' ability to lear... |