Oxonol VI
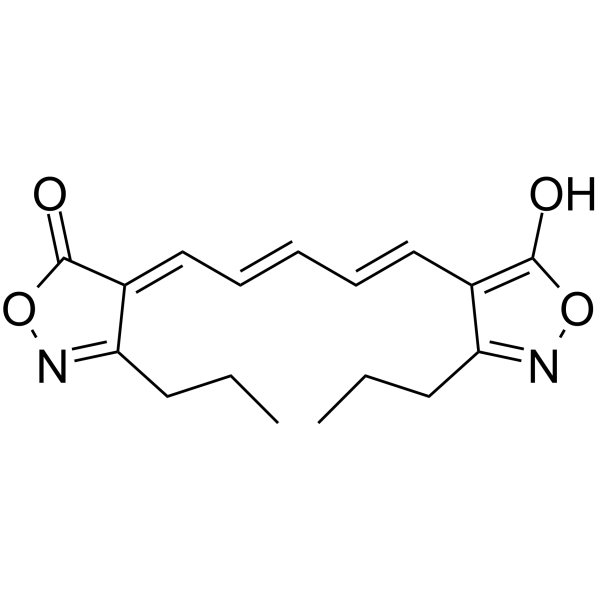
Oxonol VI structure
|
Common Name | Oxonol VI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64724-75-0 | Molecular Weight | 316.35200 | |
| Density | 1.19g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 381.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20N2O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 184.5ºC | |
|
Conserved amino acid residues of the NuoD segment important for structure and function of Escherichia coli NDH-1 (complex I).
Biochemistry 54(3) , 753-64, (2015) The NuoD segment (homologue of mitochondrial 49 kDa subunit) of the proton-translocating NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (complex I/NDH-1) from Escherichia coli is in the hydrophilic domain and bears many highly conserved amino acid residues. The three-dimensiona... |
|
|
ATP-dependent spectral response of oxonol VI in an ATP-Pi exchange complex.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 766(2) , 375-85, (1984) Energy transduction in an ATPase complex (complex V) has been studied in two reactions catalyzed by this system, i.e., ATP-dependent spectral shift of oxonol VI, and ATP-Pi exchange activity. Aurovertin alone inhibits 50% of the oxonol shift at 2 microM, and ... |
|
|
Effects of Cd2+ on ATP-driven membrane potential in beef heart mitochondrial H+-ATPase: a study using the voltage-sensitive probe oxonol VI.
Membr. Biochem. 5(3) , 225-41, (1984) Beef heart mitochondrial H+-ATPase (F1-F0) vesicles were prepared by lysolecithin extraction of ETPH. ATP-driven membrane potential was monitored indirectly by following absorbance changes of the potential-sensitive dye oxonol VI. The steady-state potential w... |
|
|
Na+-pyrophosphatase: a novel primary sodium pump.
Biochemistry 46(30) , 8872-8, (2007) Membrane-bound pyrophosphatase (PPase) is commonly believed to couple pyrophosphate (PPi) hydrolysis to H+ transport across the membrane. Here, we demonstrate that two newly isolated bacterial membrane PPases from the mesophile Methanosarcina mazei (Mm-PPase)... |
|
|
A stopped-flow kinetic study of the interaction of potential-sensitive oxonol dyes with lipid vesicles.
Biophys. Chem. 34(3) , 225-37, (1989) The interaction of the dyes oxonol V and oxonol VI with unilamellar dioleoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles was investigated using a fluorescence stopped-flow technique. On mixing with the vesicles, both dyes exhibit an increase in their fluorescence, which occu... |
|
|
Electrophysiological study with oxonol VI of passive NO3- transport by isolated plant root plasma membrane.
Biophys. J. 76(1 Pt 1) , 360-73, (1999) In contrast to animal cells, plant cells contain approximately 5-50 mM nitrate in cytosol and vacuole. The lack of specific spectroscopic probes, or suitable isotopes, impedes in vitro studies of NO3- transport. Reconstitution of root cell plasma membrane (PM... |
|
|
The use of carotenoids and oxonol VI as probes for membrane potential in proteoliposomes.
FEBS Lett. 184(1) , 96-9, (1985) Carotenoids present in lipids extracted from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6716 indicate trans-membrane potential in proteoliposomes reconstituted from these lipids and the ATPase complex isolated from the same organism. A carotenoid absorbance band shift ... |
|
|
Evidence for a selective and electroneutral K+/H(+)-exchange in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using plasma membrane vesicles.
Yeast 12(13) , 1301-13, (1996) The existence of a K+/H+ transport system in plasma membrane vesicles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is demonstrated using fluorimetric monitoring of proton fluxes across vesicles (ACMA fluorescence quenching). Plasma membrane vesicles used for this study were... |
|
|
Indications for acceleration-dependent changes of membrane potential in the flagellate Euglena gracilis.
Protoplasma 229(2-4) , 101-8, (2006) The effects of the calcium sequester EGTA on gravitactic orientation and membrane potential changes in the unicellular flagellate Euglena gracilis were investigated during a recent parabolic-flight experiment aboard of an Airbus A300. In the course of a fligh... |
|
|
Physiological parameters of gravitaxis in the flagellate Euglena gracilis obtained during a parabolic flight campaign.
J. Plant Physiol. 159(2) , 181-90, (2002) The unicellular freshwater flagellate Euglena gracilis and its close relative Astasia longa show a pronounced negative gravitaxis. Previous experiments revealed that gravitaxis is most likely mediated by an active physiological mechanism in which changes of t... |