Nortriptyline Hydrochloride
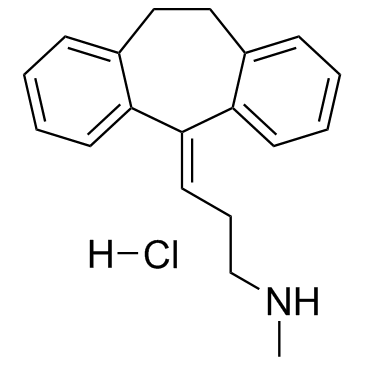
Nortriptyline Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Nortriptyline Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 894-71-3 | Molecular Weight | 299.838 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 403.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22ClN | Melting Point | 217-220ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 194.9ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Kinetic modelling for the assay of nortriptyline hydrochloride using potassium permanganate as oxidant.
AAPS PharmSciTech 16 , 569-78, (2015) Kinetic methods for accurate determination of nortriptyline hydrochloride have been described. The methods are based on the oxidation of nortriptyline hydrochloride with KMnO4 in acidic and basic media. In acidic medium, the decrease in absorbance at 525.5 nm... |
|
|
Antidepressants activate the lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA(1) to induce insulin-like growth factor-I receptor transactivation, stimulation of ERK1/2 signaling and cell proliferation in CHO-K1 fibroblasts.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 95 , 311-23, (2015) Different lines of evidence indicate that the lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor LPA1 is involved in neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and anxiety-related behavior, but little is known on whether this receptor can be targeted by neuropsychopharmacological a... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Salt effects in electromembrane extraction.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1347 , 1-7, (2014) Electromembrane extraction (EME) was performed on samples containing substantial amounts of NaCl to investigate how the presence of salts affected the recovery, repeatability, and membrane current in the extraction system. A group of 17 non-polar basic drugs ... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Quantitative aspects of electrolysis in electromembrane extractions of acidic and basic analytes.
Anal. Chim. Acta 887 , 92-100, (2015) Electrolysis is omnipresent in all electrochemical processes including electromembrane extraction (EME). The effects of electrolysis on quantitative aspects of EME were comprehensively evaluated for a set of acidic (substituted phenols) and basic (basic drugs... |
|
|
Sensitivity enhancement in direct coupling of supported liquid membrane extractions to capillary electrophoresis by means of transient isotachophoresis and large electrokinetic injections.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1389 , 1-7, (2015) Enhanced sensitivity for determination of basic drugs in body fluids was achieved by in-line coupling of extraction across supported liquid membrane (SLM) to large electrokinetic injection and transient isotachophoresis-capillary zone electrophoresis (tITP-CZ... |
|
|
Effect of the pH and the ionic strength on overloaded band profiles of weak bases onto neutral and charged surface hybrid stationary phases in reversed-phase liquid chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1282 , 113-26, (2013) This work reports on the effects of the solution pH and its ionic strength on the overloaded band profiles and the parameters of the adsorption isotherms of nortriptylinium hydrochloride on the bridge ethylene hybrid (BEH) and the charged surface hybrid (CSH)... |