Pristanic acid
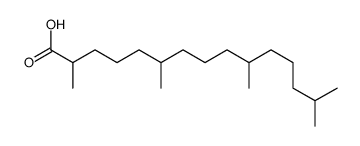
Pristanic acid structure
|
Common Name | Pristanic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1189-37-3 | Molecular Weight | 298.50400 | |
| Density | 0.882g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 408ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H38O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 14ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
New insights into the peroxisomal protein inventory: Acyl-CoA oxidases and -dehydrogenases are an ancient feature of peroxisomes.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853(1) , 111-25, (2014) Peroxisomes are ubiquitous organelles which participate in a variety of essential biochemical pathways. An intimate interrelationship between peroxisomes and mitochondria is emerging in mammals, where both organelles cooperate in fatty acid β-oxidation and ce... |
|
|
Peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme deficiency.
J. Clin. Invest. 83(3) , 771-7, (1989) Peroxisomal function was evaluated in a male infant with clinical features of neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Very long chain fatty acid levels were elevated in both plasma and fibroblasts, and beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids in cultured fibrobla... |
|
|
Branched fatty acids in dairy and beef products markedly enhance alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase expression in prostate cancer cells in vitro.
Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 12(8) , 775-83, (2003) An enzyme previously identified as alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is overexpressed in high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and in a majority (60-100%) of prostate cancers (CaPs) as compared with normal and benign hyperplastic lesions of the p... |
|
|
Clinical and biochemical characteristics of peroxisomal disorders: an update.
Eur. J. Pediatr. 153(7 Suppl 1) , S44-8, (1994) Peroxisomal disorders represent a recently recognized group of inherited diseases in man, now comprising 14 different disorders. If discussion is restricted to those peroxisomal disorders in which there is neurological involvement (thereby excluding hyperoxal... |
|
|
Differentiation of long-chain fatty acid oxidation disorders using alternative precursors and acylcarnitine profiling in fibroblasts.
Mol. Genet. Metab. 87(1) , 40-7, (2006) The differentiation of carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency (CACT) from carnitine palmitoyltransferase type II deficiency (CPT-II) and long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency from mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency ... |
|
|
Cluster of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) associated with an oil field waste site: a cross sectional study.
Environ. Health 6 , 8, (2007) This is a community comparison study that examines persons living in a subdivision exposed to petroleum products and mercury.We compared their health status and questionnaire responses to those living in another community with no known exposures of this type.... |
|
|
The influence of the branched-chain fatty acids pristanic acid and Refsum disease-associated phytanic acid on mitochondrial functions and calcium regulation of hippocampal neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes.
Neurobiol. Dis. 36(2) , 401-10, (2009) Pristanic acid and phytanic acid are branched-chain fatty acids, which play an important role in diseases with peroxisomal impairment, like Refsum disease (MIM 266500), Zellwegers syndrome and alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase deficiency (MIM 604489). Several stu... |
|
|
Effect of SCP-x gene ablation on branched-chain fatty acid metabolism.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292(3) , G939-51, (2007) Despite the importance of peroxisomal oxidation in branched-chain lipid (phytol, cholesterol) detoxification, little is known regarding the factors regulating the peroxisomal uptake, targeting, and metabolism of these lipids. Although in vitro data suggest th... |
|
|
Measurement of plasma pristanic, phytanic and very long chain fatty acids by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry for the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 798(1) , 159-62, (2003) High pressure liquid chromatography with a narrow bore C8 column has been used to separate pristanic, phytanic and very long chain fatty acids, important in the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders, for their accurate isotope dilution quantification by tandem m... |
|
|
Phytol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.
Toxicol. Pathol. 37(2) , 201-8, (2009) Phytanic acid is a branched-chain, saturated fatty acid present in high concentrations in dairy products and ruminant fat. Some other dietary fats contain lower levels of phytol, which is readily converted to phytanic acid after absorption. Phytanic acid is a... |