2-Phenylpropionaldehyde
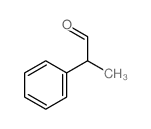
2-Phenylpropionaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | 2-Phenylpropionaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 93-53-8 | Molecular Weight | 134.17500 | |
| Density | 1.01 | Boiling Point | 201ºC (12 torr) | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O | Melting Point | 60ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 169 °F | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Reductive activation of dioxygen by a myoglobin reconstituted with a flavohemin.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(38) , 11234-5, (2002) We successfully converted myoglobin, an oxygen-storage hemoprotein, into an oxygen-activating hemoprotein like cytochrome P450s by replacing the native hemin with the artificially created flavohemin. The reconstituted myoglobin, rMb(1), was chacterized by ESI... |
|
|
Investigating the role of 2-phenylpropenal in felbamate-induced idiosyncratic drug reactions.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 17(12) , 1568-76, (2004) Felbamate (2-phenyl-1,3-propanediol dicarbamate, FBM) can cause aplastic anemia and hepatotoxicity. The mechanism of FBM-induced toxicities is unknown; however, it has been proposed that 2-phenylpropenal, a reactive metabolite of FBM, is responsible. The path... |
|
|
Synthesis and in vitro reactivity of 3-carbamoyl-2-phenylpropionaldehyde and 2-phenylpropenal: putative reactive metabolites of felbamate.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 9(8) , 1225-9, (1996) We propose that 3-carbamoyl-2-phenylpropionaldehyde is an intermediate in the metabolism of felbamate, an anti-epileptic drug with a unique profile of the therapeutic activity, and undergoes a cascade of chemical reactions responsible for the toxic properties... |
|
|
Role of glutathione S-transferases A1-1, M1-1, and P1-1 in the detoxification of 2-phenylpropenal, a reactive felbamate metabolite.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 14 , 511, (2001) Felbamate has proven to be an effective therapy for treating refractory epilepsy. However, felbamate therapy has been limited due to the associated reports of hepatotoxicity and aplastic anemia. Previous research from our laboratory has proposed 2-phenylprope... |
|
|
Interaction between human serum albumin and the felbamate metabolites 4-Hydroxy-5-phenyl-[1,3]oxazinan-2-one and 2-phenylpropenal.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15(6) , 815-24, (2002) Felbamate is an anti-epileptic drug associated with hepatotoxicity and aplastic anemia. These toxicities are believed to be mediated by the formation of the reactive species 2-phenylpropenal. 4-Hydroxy-5-phenyl-[1,3]oxazinan-2-one is a metabolic precursor for... |
|
|
Stability and comparative metabolism of selected felbamate metabolites and postulated fluorofelbamate metabolites by postmitochondrial suspensions.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 18(12) , 1842-8, (2005) Evidence has been presented suggesting that a reactive metabolite, 2-phenylpropenal (ATPAL), may be responsible for the toxicities observed during therapy with the antiepileptic drug felbamate (FBM). Formation of ATPAL from its unstable immediate precursor, 3... |