Indo-1 AM
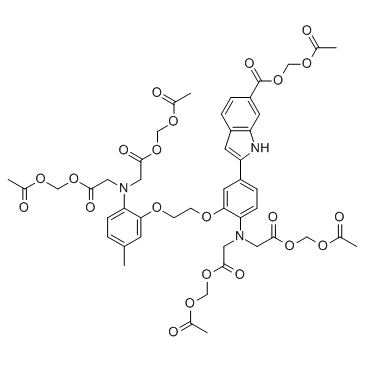
Indo-1 AM structure
|
Common Name | Indo-1 AM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 112926-02-0 | Molecular Weight | 1009.91000 | |
| Density | 1.374g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1009.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C47H51N3O22 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 564.1ºC | |
|
Quantitative TCR:pMHC Dissociation Rate Assessment by NTAmers Reveals Antimelanoma T Cell Repertoires Enriched for High Functional Competence.
J. Immunol. 195 , 356-66, (2015) Experimental models demonstrated that therapeutic induction of CD8 T cell responses may offer protection against tumors or infectious diseases providing that T cells have sufficiently high TCR/CD8:pMHC avidity for efficient Ag recognition and consequently str... |
|
|
Identification of Rare High-Avidity, Tumor-Reactive CD8+ T Cells by Monomeric TCR-Ligand Off-Rates Measurements on Living Cells.
Cancer Res. 75 , 1983-91, (2015) The avidity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) for antigenic peptides presented by the peptide-MHC (pMHC) on cells is a key parameter for cell-mediated immunity. Yet a fundamental feature of most tumor antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells is that this avidity is low. In... |
|
|
Pharmacological analysis by HOE642 and KB-R9032 of the role of Na(+)/H(+) exchange in the endothelin-1-induced Ca(2+) signalling in rabbit ventricular myocytes.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 131(3) , 638-44, (2000) The role of Na(+)/H(+) exchange in endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced increases in Ca(2+) transients and cell shortening was studied in rabbit ventricular myocytes loaded with indo-1/AM. Selective inhibitors of Na(+)/H(+) exchange HOE642 (4-isopropyl-3-methyl-sulpho... |
|
|
Cytosolic and mitochondrial [Ca2+] in whole hearts using indo-1 acetoxymethyl ester: effects of high extracellular Ca2+.
Biophys. J. 70(6) , 2571-80, (1996) Assessment of free cytosolic [Ca2+] ([Ca2+]c) using the acetoxymethyl ester (AM) form of indo-1 may be compromised by loading of indo-1 into noncytosolic compartments, primarily mitochondria. To determine the fraction of noncytosolic fluorescence in whole hea... |
|
|
Calcium signaling in airway smooth muscle cells is altered by in vitro exposure to the aldehyde acrolein.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 19(3) , 437-44, (1998) We have previously observed that acrolein administered ex vivo to isolated airways alters the subsequent airway responsiveness. To examine the cellular mechanisms involved in this alteration, we have studied the effect of acrolein exposure on calcium signalin... |
|
|
Muscarinic receptor-induced calcium responses in astroglia.
Cytometry 41(2) , 123-32, (2000) The objective of this study was to characterize and quantitate the calcium responses to cholinergic stimulation in individual primary rat cortical astrocytes and human 132 1N1 astrocytoma cells. Materials and Methods The fluorescent calcium probe Indo-1 AM an... |
|
|
Propofol-induced modifications of cardiomyocyte calcium transient and sarcoplasmic reticulum function in rats.
Anesthesiology 92(2) , 542-9, (2000) Propofol is considered to be an anesthetic agent with few or no negative inotropic effects. This study evaluated a possible direct depressant effect of propofol on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ accumulation and cardiomyocytes.The effects of propofol on intracel... |
|
|
Acetylcholine increases intracellular calcium of arterial chemoreceptor cells of adult cats.
J. Neurophysiol. 78(5) , 2388-95, (1997) Acetylcholine increases intracellular calcium of arterial chemoreceptor cells of adult cats. J. Neurophysiol. 78: 2388-2395, 1997. Several neurotransmitters have been reported to play important roles in the chemoreception of the carotid body. Among them acety... |
|
|
Modulation of the kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations by calcium entry in pituitary gonadotrophs.
Biophys. J. 72(2 Pt 1) , 698-707, (1997) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) binds to its receptor channels and causes liberation of Ca2+ from intracellular stores, frequently in an oscillatory manner. In addition to InsP3, the activation and inactivation properties of these intracellular channels ... |
|
|
Species dependence of mitochondrial calcium transients during excitation-contraction coupling in isolated cardiomyocytes.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 263(2) , 554-9, (1999) Whether mitochondrial Ca(2+) transport is rapid enough to respond to changes in cytosolic [Ca(2+)] ([Ca(2+)](c)) which occur during excitation-contraction coupling in the heart is controversial; different results wereobtained with different techniques and dif... |