Isoprenaline hydrochloride
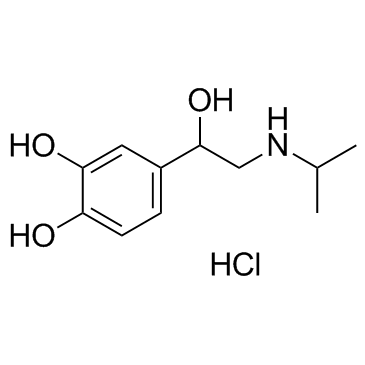
Isoprenaline hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Isoprenaline hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51-30-9 | Molecular Weight | 247.719 | |
| Density | 1.324 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 417.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H18ClNO3 | Melting Point | 165-175 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 179.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Cross-talk from β-adrenergic receptors modulates α2A-adrenergic receptor endocytosis in sympathetic neurons via protein kinase A and spinophilin.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(40) , 29193-205, (2013) Inter-regulation of adrenergic receptors (ARs) via cross-talk is a long appreciated but mechanistically unclear physiological phenomenon. Evidence from the AR literature and our own extensive studies on regulation of α2AARs by the scaffolding protein spinophi... |
|
|
β-Adrenergic receptors activate exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac), translocate Munc13-1, and enhance the Rab3A-RIM1α interaction to potentiate glutamate release at cerebrocortical nerve terminals.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(43) , 31370-85, (2013) The adenylyl cyclase activator forskolin facilitates synaptic transmission presynaptically via cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). In addition, cAMP also increases glutamate release via PKA-independent mechanisms, although the downstream presynaptic targets ... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Protein kinetic signatures of the remodeling heart following isoproterenol stimulation.
J. Clin. Invest. 124(4) , 1734-44, (2014) Protein temporal dynamics play a critical role in time-dimensional pathophysiological processes, including the gradual cardiac remodeling that occurs in early-stage heart failure. Methods for quantitative assessments of protein kinetics are lacking, and despi... |
|
|
β3-Adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation of rat and human urinary bladder: roles of BKCa channels and Rho kinase.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 388 , 749-59, (2015) Previous studies suggest that the large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BKCa) channel and Rho-kinase play major roles in the control of urinary bladder tone. Here, we investigated their involvement in β-adrenoceptor (AR)-mediated relaxation of rat and huma... |
|
|
Tramadol inhibits the contractility of isolated human myometrium.
Auton. Autacoid Pharmacol. 33(1-2) , 1-5, (2013) This study was conducted to determine whether the atypical opioid analgesic tramadol inhibits the contractility of isolated non-pregnant human myometrium. Ten strips of non-pregnant human myometrium stimulated with 55 mm potassium chloride (KCl) were treated ... |
|
|
Autophagy protects against dasatinib-induced hepatotoxicity via p38 signaling.
Oncotarget 6(8) , 6203-17, (2015) Liver dysfunction is a common side effect associated with the treatment of dasatinib and its mechanism is poorly understood. Autophagy has been thought to be a potent survival or death factor for liver dysfunction, which may shed the light on a novel strategy... |