Acid violet 17
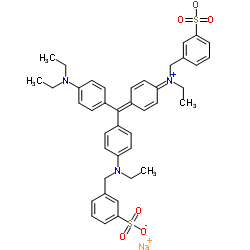
Acid violet 17 structure
|
Common Name | Acid violet 17 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4129-84-4 | Molecular Weight | 761.924 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C41H44N3NaO6S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
An investigation into the enhancement of fingermarks in blood on fruit and vegetables.
Sci. Justice 53(3) , 321-7, (2013) A number of studies have reported the successful enhancement of latent fingermarks on fruit and vegetables. A study was set up to identify the most effective technique for the enhancement of fingermarks in blood on various fruit and vegetables. The enhancemen... |
|
|
Comparative mutagenicity of two triarylmethane food dyes in Salmonella, Saccharomyces and Drosophila.
Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 19(4) , 419-24, (1981)
|
|
|
[Development and clinical evaluation of a new urinary protein test paper (URINE-TP)].
Rinsho Byori. 39(4) , 398-404, (1991) Because standard urinary protein test paper reacts more strongly to albumin than to globulin, we attempted to develop a test paper sensitive to globulin by applying chromatic analysis principles used in quantitative analysis of urinary protein. We developed a... |
|
|
Removal of Acid Violet 17 from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from sunflower seed hull.
J. Hazard. Mater. 151(2-3) , 316-22, (2008) The adsorption of Acid Violet 17 (AV17) was carried out using various activated carbons prepared from sunflower seed hull (SSH), an agricultural solid waste by-product. The effect of parameters such as agitation time, initial dye concentration, adsorbent dosa... |
|
|
Orange peel as an adsorbent in the removal of acid violet 17 (acid dye) from aqueous solutions.
Waste Manag. 21(1) , 105-10, (2001) The effectiveness of orange peel in adsorbing Acid violet 17 from aqueous solutions has been studied as a function of agitation time, adsorbent dosage, initial dye concentration and pH. The adsorption follows both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. The adsorp... |
|
|
Bioaccumulation of the synthetic dye Basic Violet 3 and heavy metals in single and binary systems by Candida tropicalis grown in a sugarcane bagasse extract medium: modelling optimal conditions using response surface methodology (RSM) and inhibition kinetics.
J. Hazard. Mater. 186(2-3) , 1541-52, (2011) Single and binary effects of dye Basic Violet 3 and heavy metals, 'namely', Pb(II) and Cd(II), were investigated for their role in dye and heavy metal bioaccumulation by Candida tropicalis that was grown in a sugarcane bagasse extract medium containing 8 g/L,... |
|
|
Laccase/mediator assisted degradation of triarylmethane dyes in a continuous membrane reactor.
J. Biotechnol. 143(1) , 69-78, (2009) Laccase/mediator systems are important bioremediation agents as the rates of reactions can be enhanced in the presence of the mediators. The decolorization mechanism of two triarylmethane dyes, namely, Basic Green 4 and Acid Violet 17 is reported using Cyathu... |
|
|
Fast and sensitive protein staining with colloidal acid violet 17 following isoelectric focusing in carrier ampholyte generated and immobilized pH gradients.
Electrophoresis 9(9) , 488-96, (1988) A new method is described for fast and sensitive staining of proteins following isoelectric focusing in carrier ampholyte and immobilized pH gradient polyacrylamide gels. After fixation with trichloroacetic acid the gels are stained for 5-10 min with 0.1-0.2%... |
|
|
Highly sensitive method for staining protein fractions on cellulose acetate membrane with acid violet 17.
Clin. Chem. 32(12) , 2209, (1986)
|
|
|
Investigation of the retinal biocompatibility of acid violet for chromovitrectomy.
Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 251(4) , 1115-21, (2013) The primary objective was to investigate the retinal biocompatibility of acid violet (AV) as a vital dye for chromovitrectomy. The secondary objective was to evaluate the capacity of AV to stain the anterior capsule of the lens.An amount of 0.05 ml of 0.25 g/... |