Cephalexin
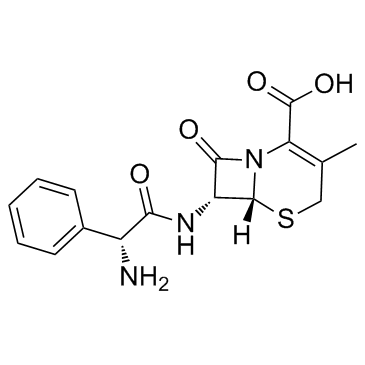
Cephalexin structure
|
Common Name | Cephalexin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 15686-71-2 | Molecular Weight | 347.389 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 727.4±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H17N3O4S | Melting Point | 196-198°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 393.7±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Interaction of Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin with human TLR2: identification of the TLR2-binding domain.
APMIS 123(2) , 156-62, (2015) Filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA) is a major adhesion and virulence factor of Bordetella pertussis and also a main component of acellular pertussis vaccines. Interaction of FHA with different receptors on human epithelial and immune cells facilitates entrance a... |
|
|
Disruption of an M. tuberculosis membrane protein causes a magnesium-dependent cell division defect and failure to persist in mice.
PLoS Pathog. 11(2) , e1004645, (2015) The identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes necessary for persistence in vivo provides insight into bacterial biology as well as host defense strategies. We show that disruption of M. tuberculosis membrane protein PerM (Rv0955) resulted in an IFN-γ... |
|
|
Purification and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacillithiol transferase BstA.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(9) , 2851-61, (2014) Gram-positive bacteria in the phylum Firmicutes synthesize the low molecular weight thiol bacillithiol rather than glutathione or mycothiol. The bacillithiol transferase YfiT from Bacillus subtilis was identified as a new member of the recently discovered Din... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of 38 veterinary antibiotic residues in raw milk by UPLC-MS/MS.
Food Chem. 181 , 119-26, (2015) A selective and rapid method has been developed to determine, simultaneously, 38 veterinary antibiotic residues in raw milk by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). One milliliter of raw milk was diluted with 0.5 ... |
|
|
Emerging organic contaminants in coastal waters: anthropogenic impact, environmental release and ecological risk.
Mar. Pollut. Bull. 85(2) , 391-9, (2014) This study provides a first estimate of the sources, distribution, and risk presented by emerging organic contaminants (EOCs) in coastal waters off southwestern Taiwan. Ten illicit drugs, seven nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), five antibiotics, ... |
|
|
Monitoring and removal of residual phthalate esters and pharmaceuticals in the drinking water of Kaohsiung City, Taiwan.
J. Hazard. Mater. 277 , 53-61, (2014) This study monitored the occurrence and removal efficiencies of 8 phthalate esters (PAEs) and 13 pharmaceuticals present in the drinking water of Kaohsiung City, Taiwan. The simultaneous electrocoagulation and electrofiltration (EC/EF) process was used to rem... |
|
|
Isolation of Escherichia coli strains with AcrAB-TolC efflux pump-associated intermediate interpretation or resistance to fluoroquinolone, chloramphenicol and aminopenicillin from dogs admitted to a university veterinary hospital.
J. Vet. Med. Sci. 76(7) , 937-45, (2014) Understanding the prevalence of antimicrobial-resistance and the relationship between emergence of resistant bacteria and clinical treatment can facilitate design of effective treatment strategies. We here examined antimicrobial susceptibilities of Escherichi... |
|
|
Development and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the detection and cleanup of benzylpenicillin in milk.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(35) , 8814-21, (2014) A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was designed for benzylpenicillin via suspension polymerization. The specific absorption of benzylpenicillin to the MIP, applied in a molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction (MISPE), was compared to the nonspecific b... |
|
|
Characterization of cefalexin degradation capabilities of two Pseudomonas strains isolated from activated sludge.
J. Hazard. Mater. 282 , 158-64, (2014) Pharmaceuticals have recently been regarded as contaminants of emerging concern. To date, there is limited knowledge about antibiotic-degrading microorganisms in conventional activated sludge treatment systems and their characteristics toward antibiotic degra... |
|
|
Antibiotic prophylaxis for ED patients with simple hand lacerations: a feasibility randomized controlled trial.
Am. J. Emerg. Med. 32(7) , 768-71, (2014) The benefit of antibiotic prophylaxis for simple hand lacerations (lacerations that do not involve special structures) has not been adequately studied.To assess the feasibility of a randomized controlled trial to determine the role of antibiotic prophylaxis i... |