epi-Inositol
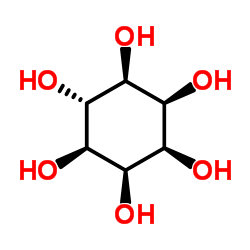
epi-Inositol structure
|
Common Name | epi-Inositol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 488-58-4 | Molecular Weight | 180.156 | |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 291.3±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O6 | Melting Point | 304°C(dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 143.4±21.9 °C | |
|
Synthesis of allo- and epi-inositol via the NHC-catalyzed carbocyclization of carbohydrate-derived dialdehydes.
J. Org. Chem. 79(11) , 5088-96, (2014) A synthesis of carbocyclic sugars from carbohydrate-derived dialdehydes using organocatalysis has been developed. Sorbitol, mannitol, and galactitol were converted via 1,6-tritylation, perbenzylation or permethylation, detritylation, and Swern oxidation into ... |
|
|
Synthesis of phosphatidylinositols having various inositol stereoisomers by engineered phospholipase D.
J. Biosci. Bioeng. 109(4) , 337-40, (2010) Phospholipase D-mediated synthesis of phosphatidylinositols having various inositol stereoisomers was studied. Seven inositol stereoisomers were tested, all of which were found to be substrates of the enzyme, generating the corresponding phosphatidylinositols... |
|
|
Cyclohexanehexol inhibitors of Abeta aggregation prevent and reverse Alzheimer phenotype in a mouse model.
Nat. Med. 12(7) , 801-8, (2006) When given orally to a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease, cyclohexanehexol stereoisomers inhibit aggregation of amyloid beta peptide (Abeta) into high-molecular-weight oligomers in the brain and ameliorate several Alzheimer disease-like phenotypes i... |
|
|
Epi-inositol regulates expression of the yeast INO1 gene encoding inositol-1-P synthase.
Mol. Psychiatry 7(2) , 174-80, (2002) Myo-inositol exerts behavioral effects in animal models of psychiatric disorders and is effective in clinical trials in psychiatric patients. Interestingly, epi-inositol exerts behavioral effects similar to myo-inositol, even though epi-inositol is not a subs... |
|
|
Inositol stereoisomers stabilize an oligomeric aggregate of Alzheimer amyloid beta peptide and inhibit abeta -induced toxicity.
J. Biol. Chem. 275(24) , 18495-502, (2000) Inositol has 8 stereoisomers, four of which are physiologically active. myo-Inositol is the most abundant isomer in the brain and more recently shown that epi- and scyllo-inositol are also present. myo-Inositol complexes with Abeta42 in vitro to form a small ... |
|
|
Topological and functional characterization of an insect gustatory receptor.
PLoS ONE 6(8) , e24111, (2011) Insect gustatory receptors are predicted to have a seven-transmembrane structure and are distantly related to insect olfactory receptors, which have an inverted topology compared with G-protein coupled receptors, including mammalian olfactory receptors. In co... |
|
|
A recombinant α-(2→3)-sialyltransferase with an extremely broad acceptor substrate specificity fromPhotobacteriumsp. JT-ISH-224 can transferN-acetylneuraminic acid to inositols
Carbohydr. Res. 345(17) , 2485-90, (2010) We confirmed that a recombinant α-(2→3)-sialyltransferase cloned from Photobacterium sp. JT-ISH-224 recognizes inositols having a structure corresponding to the C-3 and C-4 of a galactopyranoside moiety, such as epi-, 1d-chiro, myo-, and muco-inositol, as acc... |
|
|
Sodium/myo-Inositol transporters: substrate transport requirements and regional brain expression in the TgCRND8 mouse model of amyloid pathology.
PLoS ONE 6 , e24032, (2011) Inositol stereoisomers, myo- and scyllo-inositol, are known to enter the brain and are significantly elevated following oral administration. Elevations in brain inositol levels occur across a concentration gradient as a result of active transport from the per... |