(-)-2-Chloropropanoic acid
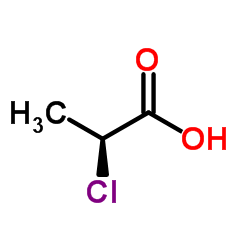
(-)-2-Chloropropanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | (-)-2-Chloropropanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 29617-66-1 | Molecular Weight | 108.524 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 189.0±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H5ClO2 | Melting Point | 4ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 101.7±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Haloalkanoate dehalogenase II (DehE) of a Rhizobium sp.--molecular analysis of the gene and formation of carbon monoxide from trihaloacetate by the enzyme.
Eur. J. Biochem. 250(3) , 789-93, (1997) A 3-kb EcoRI fragment of genomic DNA from a Rhizobium sp. cloned into pUC19 endowed Escherichia coli K-12 with the ability to grow, albeit slowly, with 2-chloropropionic acid as substrate. The construct expressed weakly a gene that encoded a non-stereospecifi... |
|
|
Direct determination of the enantiomeric purity or enantiomeric composition of methylpropionates using a single capacitive microsensor.
Anal. Chem. 81(5) , 1969-75, (2009) Capacitive enantioselective sensors have been demonstrated to provide antipodal signals upon dosage of, e.g., the enantiomers of methyl lactate or methyl-2-chloropropionate. In a next step, these sensors have been used to not only qualitatively determine the ... |
|
|
Use of structure-activity relationships for probing biochemical mechanisms: glutathione transferase zeta conjugation of haloacids.
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 500 , 23-31, (2001)
|
|
|
The absence of cerebellar granule cell necrosis in the mouse following L-2-chloropropionic acid administration.
Arch. Toxicol. 74(9) , 547-54, (2000) Oral administration of L-2-chloropropionic acid (L-CPA) to rats either as a single dose (750 mg/kg) or daily doses (250 mg/kg per day for 3 days) produces selective necrosis to the granule cell layer of the cerebellum. As part of a study to understand the mec... |
|
|
Isolation, characterization and identification of a Paracoccus sp. 2-haloacid-degrading bacterium from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perlevis.
J. Basic Microbiol. 51(3) , 318-24, (2011) A 2-haloacid dehalogenase-producing bacterium, designated DEH99, was isolated from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perlevis using a modified enrichment medium and a pH indicator method. DEH99 could degrade only half of the racemic mixture 2-chloropropionic aci... |
|
|
Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of β-chlorinated aliphatic acid in Bacillus sp. CGMCC no. 4196.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 90(2) , 689-96, (2011) In this study, a bacterial Bacillus sp. CGMCC no. 4196 was isolated from mud. This strain exhibited the ability to degrade high concentration of 3-chloropropionate (3-CPA, 120 mM) or 3-chlorobutyrate (30 mM), but not chloroacetate or 2-chloropropionate (2-CPA... |
|
|
Biochemical and neurotoxicological effects of L-2-chloropropionic acid on rodent brain.
J. Neurochem. 73(1) , 362-71, (1999) L-2-Chloropropionic acid (L-CPA) is selectively toxic to cerebellar granule cells; necrosis is first observed in rats 36 h after L-CPA administration (750 mg/kg p.o.) and becomes marked by 48 h. L-CPA has also been shown to activate the mitochondrial pyruvate... |
|
|
Neuroprotective effects of MK-801 on L-2-chloropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity.
J. Neurochem. 76(4) , 1057-65, (2001) L-2-Chloropropionic acid is selectively toxic to the cerebellum in rats; the granule cell necrosis observed within 48 h can be prevented by prior administration of MK-801. Short-term treatment (2 h) with L-2-chloropropionic acid has also been shown to activat... |
|
|
Re-evaluation of archival material for neuronal cell injury produced by L-2-chloropropionic acid in the rat brain.
Neurotoxicology 25(6) , 1031-40, (2004) Previous studies have shown that L-2-chloropropionic acid (L-CPA) produces necrosis to cerebellar granule cells with some associated Purkinje cell damage in the rat. We have re-evaluated the neuropathology using the original sections and fresh sections from a... |
|
|
Toxic effect of L-2-chloropropionate on cultured rat cerebellar granule cells is ameliorated after inhibition of reactive oxygen species formation.
J. Neurosci. Res. 66(5) , 992-7, (2001) Oral administration of rats to L-2-chloropropionate (L-CPA) causes selective necrosis to the granule cell layer of the cerebellum in vivo and to cultured rat cerebellar granule cells in vitro. The present study was conducted to characterize the involvement of... |