Meropenem trihydrate
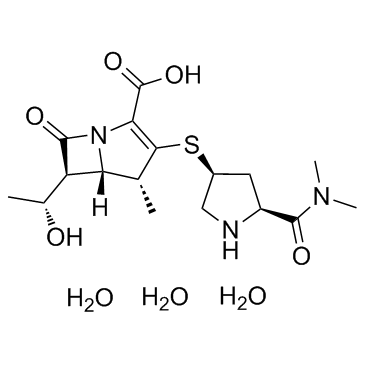
Meropenem trihydrate structure
|
Common Name | Meropenem trihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 119478-56-7 | Molecular Weight | 383.462 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 627.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H31N3O8S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 333.2±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Disruption of an M. tuberculosis membrane protein causes a magnesium-dependent cell division defect and failure to persist in mice.
PLoS Pathog. 11(2) , e1004645, (2015) The identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes necessary for persistence in vivo provides insight into bacterial biology as well as host defense strategies. We show that disruption of M. tuberculosis membrane protein PerM (Rv0955) resulted in an IFN-γ... |
|
|
Genetic acquisition of NDM gene offers sustainability among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical settings.
PLoS ONE 10(1) , e0116611, (2015) New Delhi metallo β-lactamases are one of the most significant emerging resistance determinants towards carbapenem drugs. Their persistence and adaptability often depends on their genetic environment and linkage. This study reports a unique and novel arrangem... |
|
|
Virulence attributes in Brazilian clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 304(8) , 990-1000, (2014) Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic human pathogen responsible for causing a huge variety of acute and chronic infections with significant levels of morbidity and mortality. Its success as a pathogen comes from its genetic/metabolic plasticity, intrins... |
|
|
Clonal diversity of Acinetobacter baumannii from diabetic patients in Saudi Arabian hospitals.
J. Med. Microbiol. 63(Pt 11) , 1460-6, (2014) Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CR-AB) represents a major health-care problem, causing high rates of morbidity and mortality. This study investigated the clonality of CR-AB isolated from diabetic patients from different regions in Saudi Arabia, ... |
|
|
Detection of OXA-48-type carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in diagnostic laboratories can be enhanced by addition of bicarbonates to cultivation media or reaction buffers.
Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 60(2) , 119-29, (2015) Carbapenemase-mediated resistance to carbapenems in Enterobacteriaceae has become the main challenge in the treatment and prevention of infections recently. The partially unnoticed spread of OXA-48-type carbapenemase producers is usually assigned to low minim... |
|
|
Quantification of piperacillin, tazobactam, cefepime, meropenem, ciprofloxacin and linezolid in serum using an isotope dilution UHPLC-MS/MS method with semi-automated sample preparation.
Clin. Chem. Lab Med. 53(5) , 781-91, (2015) Recent studies have demonstrated highly variable blood concentrations of piperacillin, tazobactam, cefepime, meropenem, ciprofloxacin and linezolid in critically ill patients with a high incidence of sub-therapeutic levels. Consequently, therapeutic drug moni... |
|
|
Antibiotics and renal branching morphogenesis: comparison of toxicities.
Pediatr. Res. 76(6) , 508-14, (2014) Many premature born neonates receive antibiotic drugs to treat infections, which are applied during active nephrogenesis. We studied the impact of clinical concentrations of gentamicin and alternatives, ceftazidime and meropenem, on ureteric branching.Mice me... |
|
|
Tolerability of aztreonam and carbapenems in patients with IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to penicillins.
J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 135(4) , 972-6, (2015) Studies performed on samples larger than 100 subjects with a documented IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to penicillins have demonstrated a cross-reactivity rate of approximately 1% between penicillins and both imipenem and meropenem, whereas a single study foun... |
|
|
In vitro antibacterial activity of AZD0914, a new spiropyrimidinetrione DNA gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitor with potent activity against Gram-positive, fastidious Gram-Negative, and atypical bacteria.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59(1) , 467-74, (2014) AZD0914 is a new spiropyrimidinetrione bacterial DNA gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitor with potent in vitro antibacterial activity against key Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, and... |
|
|
An in vitro deletion in ribE encoding lumazine synthase contributes to nitrofurantoin resistance in Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(12) , 7225-33, (2014) Nitrofurantoin has been used for decades for the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs), but clinically significant resistance in Escherichia coli is uncommon. Nitrofurantoin concentrations in the gastrointestinal tract tend to be low, which might facil... |