CGP 55845 hydrochloride
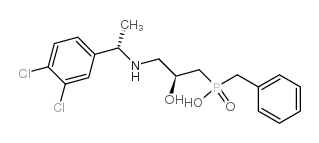
CGP 55845 hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | CGP 55845 hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 149184-22-5 | Molecular Weight | 402.25200 | |
| Density | 1.332g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 647.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H22Cl2NO3P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 345.6ºC | |
|
Persistent sodium current drives conditional pacemaking in CA1 pyramidal neurons under muscarinic stimulation.
J. Neurosci. 33(38) , 15011-21, (2013) Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons are normally quiescent but can fire spontaneously when stimulated by muscarinic agonists. In brain slice recordings from mouse CA1 pyramidal neurons, we examined the ionic basis of this activity using interleaved current-clam... |
|
|
Dopamine triggers heterosynaptic plasticity.
J. Neurosci. 33(16) , 6759-65, (2013) As a classic neuromodulator, dopamine has long been thought to modulate, rather than trigger, synaptic plasticity. In contrast, our present results demonstrate that within the parallel projections of dopaminergic and GABAergic terminals from the ventral tegme... |
|
|
Increased astrocytic ATP release results in enhanced excitability of the hippocampus.
Glia 61(2) , 210-24, (2013) Astrocytes, a major subtype of glia, interact with neurons as a supportive partner supplying energy sources and growth factors. Astrocytes regulate the activity of neighboring neurons by releasing chemical transmitters (gliotransmitters). However, the precise... |
|
|
Interneurons provide circuit-specific depolarization and hyperpolarization.
J. Neurosci. 32(12) , 4224-9, (2012) Perisoma-inhibiting interneurons (PIIs) control fundamental aspects of cortical network function by means of their GABAergic output synapses. However, whether they depolarize or hyperpolarize their target cells in the mature circuitry remains controversial. B... |
|
|
M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors regulate long-term potentiation at hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cell synapses in an input-specific fashion.
J. Neurophysiol. 108(1) , 91-100, (2012) Muscarinic receptors have long been known as crucial players in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory, but our understanding of the cellular underpinnings and the receptor subtypes involved lags well behind. This holds in particular for the hippocampal CA... |
|
|
Cortical inhibition reduces information redundancy at presentation of communication sounds in the primary auditory cortex.
J. Neurosci. 33(26) , 10713-28, (2013) In all sensory modalities, intracortical inhibition shapes the functional properties of cortical neurons but also influences the responses to natural stimuli. Studies performed in various species have revealed that auditory cortex neurons respond to conspecif... |
|
|
Presynaptic calcium influx controls neurotransmitter release in part by regulating the effective size of the readily releasable pool.
J. Neurosci. 33(11) , 4625-33, (2013) The steep calcium dependence of synaptic strength that has been observed at many synapses is thought to reflect a calcium dependence of the probability of vesicular exocytosis (p), with the cooperativity of three to six corresponding to the multiple calcium i... |
|
|
Calcium microdomains near R-type calcium channels control the induction of presynaptic long-term potentiation at parallel fiber to purkinje cell synapses.
J. Neurosci. 31(14) , 5235-43, (2011) R-type calcium channels in postsynaptic spines signal through functional calcium microdomains to regulate a calcium/calmodulin-sensitive potassium channel that in turn regulates postsynaptic hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP). Here, we ask whether R-typ... |
|
|
Astrocytes control GABAergic inhibition of neurons in the mouse barrel cortex.
J. Physiol. 589(Pt 5) , 1159-72, (2011) Astrocytes in the barrel cortex respond with a transient Ca2+ increase to neuronal stimulation and this response is restricted to the stimulated barrel field. In the present study we suppressed the astrocyte response by dialysing these cells with the Ca2+ che... |
|
|
Ovarian hormone deficiency reduces intrinsic excitability and abolishes acute estrogen sensitivity in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.
J. Neurosci. 31(7) , 2638-48, (2011) Premature and uncompensated loss of ovarian hormones following ovariectomy (OVX) elevates the risks of cognitive impairment and dementia. These risks are prevented with estrogen (E(2))-containing hormone replacement therapy initiated shortly following OVX but... |