Astrocytes control GABAergic inhibition of neurons in the mouse barrel cortex.
B Benedetti, V Matyash, H Kettenmann
Index: J. Physiol. 589(Pt 5) , 1159-72, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Astrocytes in the barrel cortex respond with a transient Ca2+ increase to neuronal stimulation and this response is restricted to the stimulated barrel field. In the present study we suppressed the astrocyte response by dialysing these cells with the Ca2+ chelator BAPTA. Electrical stimulation triggered a depolarization in stellate or pyramidal ‘regular spiking' neurons from cortex layer 4 and 2/3 and this response was augmented in amplitude and duration after astrocytes were dialysed with BAPTA. Combined blockade of GABAA and GABAB receptors mimicked the effect of BAPTA dialysis, while glutamate receptor blockers had no effect. Moreover, the frequency of spontaneous postsynaptic currents was increased after BAPTA dialysis. Outside the range of BAPTA dialysis astrocytes responded with a Ca2+ increase, but in contrast to control, the response was no longer restricted to one barrel field. Our findings indicate that astrocytes control neuronal inhibition in the barrel cortex.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
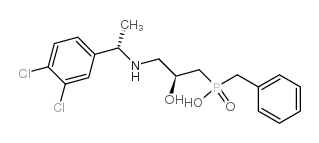 |
CGP 55845 hydrochloride
CAS:149184-22-5 |
C18H22Cl2NO3P |
|
Persistent sodium current drives conditional pacemaking in C...
2013-09-18 [J. Neurosci. 33(38) , 15011-21, (2013)] |
|
Dopamine triggers heterosynaptic plasticity.
2013-04-17 [J. Neurosci. 33(16) , 6759-65, (2013)] |
|
Increased astrocytic ATP release results in enhanced excitab...
2013-02-01 [Glia 61(2) , 210-24, (2013)] |
|
Interneurons provide circuit-specific depolarization and hyp...
2012-03-21 [J. Neurosci. 32(12) , 4224-9, (2012)] |
|
M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors regulate long-term pot...
2012-07-01 [J. Neurophysiol. 108(1) , 91-100, (2012)] |