Echinacoside
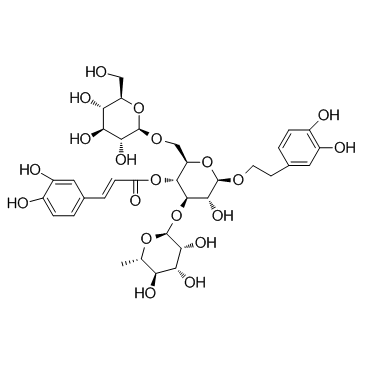
Echinacoside structure
|
Common Name | Echinacoside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 82854-37-3 | Molecular Weight | 786.728 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1062.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H46O20 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 327.9±27.8 °C | |
|
Plantago lanceolata L. water extract induces transition of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and increases tensile strength of healing skin wounds.
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67(1) , 117-25, (2014) Although the exact underlying mechanisms are still unknown, Plantago lanceolata L. (PL) water extracts are frequently used to stimulate wound healing and to drain abscesses. Therefore, in this experimental study the effect of PL water extract on skin wound he... |
|
|
Echinacoside Induces Apoptosis in Human SW480 Colorectal Cancer Cells by Induction of Oxidative DNA Damages.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 14655-68, (2015) Echinacoside is a natural compound with potent reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging and anti-oxidative bioactivities, which protect cells from oxidative damages. As cancer cells are often under intense oxidative stress, we therefore tested if Echinacoside... |
|
|
Echinacoside induces apoptotic cancer cell death by inhibiting the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1.
Onco. Targets Ther. 8 , 3649-64, (2015) Inhibition of the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme MTH1 causes extensive oxidative DNA damages and apoptosis in cancer cells and hence may be used as an anticancer strategy. As natural products have been a rich source of medicinal chemicals, in the present s... |
|
|
Production of acteoside from Cistanche tubulosa by β-glucosidase.
Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 24(2) , 135-41, (2011) Acteoside and echinacoside are the major active components of Herba Cistanches. Facilitated β-glucosidation was investigated as a means of increasing harvest of acteoside from Cistanche tubulosa. Fresh Cistanche tubulosa was treated by microwave moisture proc... |
|
|
Antiosteoporotic activity of echinacoside in ovariectomized rats.
Phytomedicine 20(6) , 549-57, (2013) Echinacoside (ECH), isolated from Cistanche tubulosa (Schrenk) R. Wight stems, has been reported to enhance bone regeneration in MC3T3-E1 cells in vitro. The objectives of this study were to investigate the antiosteoporotic effect of ECH on bone metabolism in... |
|
|
Metabolism of echinacoside, a good antioxidant, in rats: isolation and identification of its biliary metabolites.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 37(2) , 431-8, (2009) Echinacoside (ECH) is one of the major active phenylethanoid glycosides (PEGs) in famous traditional Chinese medicine, Herba Cistanches. Although it has various bioactivities, such as antioxidation, neuroprotection, and hepatoprotection, knowledge about its m... |
|
|
Neurotrophic and neurorescue effects of Echinacoside in the subacute MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Brain Res. 1346 , 224-36, (2010) Many experiments support the notion that augmentation of neurotrophic factors' (NTFs) activity, especially glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) could prevent or halt the progress of neurodegeneration ... |
|
|
Inhibitory effect of acteoside isolated from Cistanche tubulosa on chemical mediator release and inflammatory cytokine production by RBL-2H3 and KU812 cells.
Planta Med. 76(14) , 1512-8, (2010) The immediate-type allergic reaction is involved in many allergic diseases such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, and sinusitis. In this study, we investigated the effect of acteoside extracted from CISTANCHE TUBULOSA (Schrenk) R. Wight on the basophilic cell-med... |
|
|
Protective effects of echinacoside, one of the phenylethanoid glycosides, on H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells.
Planta Med. 75(14) , 1499-504, (2009) We have investigated the protective effects of echinacoside (ECH), one of the phenylethanoid glycosides, on H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in the rat pheochromocytoma cell line (PC12 cells). Our data show that application of ECH to H(2)O(2)-injured PC12 cells ... |
|
|
Transient exposure to echinacoside is sufficient to activate Trk signaling and protect neuronal cells from rotenone.
J. Neurochem. 124(4) , 571-80, (2013) Neurotrophins exert their physiological functions mainly through Trk receptors, and the neurotrophic signaling network is critical to the survival of neurons. However, therapeutic use of neurotrophins in treating neurodegenerative diseases is hampered by a nu... |