Protective effects of echinacoside, one of the phenylethanoid glycosides, on H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells.
Rong Kuang, Yiguo Sun, Wei Yuan, Li Lei, Xiaoxiang Zheng
Index: Planta Med. 75(14) , 1499-504, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We have investigated the protective effects of echinacoside (ECH), one of the phenylethanoid glycosides, on H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in the rat pheochromocytoma cell line (PC12 cells). Our data show that application of ECH to H(2)O(2)-injured PC12 cells (HIPCs) increased cell viability and decreased the apoptotic ratio. Flow cytometry (FCM) and laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) analysis suggested that ECH exerted its inhibitory effects on the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the accumulation of intracellular free Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)]i). In addition, ECH elevated the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) in HIPCs. Furthermore, Western blot analysis revealed that ECH prevented an H(2)O(2)-induced increase of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio by down-regulating Bax protein expression and upregulating Bcl-2 protein expression. In summary, ECH showed significant neuroprotective effects on HIPCs through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, and could be a potential candidate for intervention in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart, New York.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
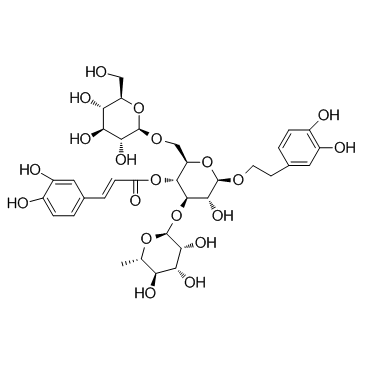 |
Echinacoside
CAS:82854-37-3 |
C35H46O20 |
|
Plantago lanceolata L. water extract induces transition of f...
2015-01-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67(1) , 117-25, (2014)] |
|
Echinacoside Induces Apoptosis in Human SW480 Colorectal Can...
2015-01-01 [Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 14655-68, (2015)] |
|
Echinacoside induces apoptotic cancer cell death by inhibiti...
2015-01-01 [Onco. Targets Ther. 8 , 3649-64, (2015)] |
|
Production of acteoside from Cistanche tubulosa by β-glucosi...
2011-04-01 [Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 24(2) , 135-41, (2011)] |
|
Antiosteoporotic activity of echinacoside in ovariectomized ...
2013-04-15 [Phytomedicine 20(6) , 549-57, (2013)] |