Clindamycin Hydrochloride
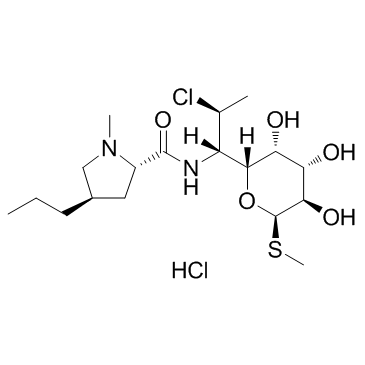
Clindamycin Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Clindamycin Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21462-39-5 | Molecular Weight | 461.444 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 628.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H34Cl2N2O5S | Melting Point | 141°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 333.6ºC | |
|
Performance characterization of a quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for 12 macrolide and lincosamide antibiotics in salmon, shrimp and tilapia.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 967 , 203-10, (2014) This paper describes an extension and performance characterization of a quantitative confirmatory multi-residue liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for residues of macrolide and lincosamide antibiotics, originally validated for application ... |
|
|
Development of a method to quantify clindamycin in vitreous humor of rabbits' eyes by UPLC-MS/MS: application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study and in vivo ocular biocompatibility evaluation.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 346-52, (2015) Ocular toxoplasmosis may result in uveitis in the posterior segment of the eye, leading to severe visual complications. Clindamycin-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) implants could be applied to treat the ocular toxoplasmosis. In this study, the pharma... |
|
|
A biodegradable antibiotic-impregnated scaffold to prevent osteomyelitis in a contaminated in vivo bone defect model.
Eur. Cell. Mater. 27 , 332-49, (2014) Open fractures are at risk of serious infection and, if infected, require several surgical interventions and courses of systemic antibiotics. We investigated a new injectable formulation that simultaneously hardens in vivo to form a porous scaffold for bone r... |
|
|
Rare variations in IL36RN in severe adverse drug reactions manifesting as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 133(7) , 1904-7, (2013)
|
|
|
Enantioseparation of basic chiral compounds on a clindamycin phosphate-silica/zirconia hybrid monolith by capillary electrochromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 289-93, (2014) An organic-inorganic silica/zirconia hybrid monolithic capillary column was prepared by sol-gel process in a fused-silica capillary by using triethoxysilylpropylcarbamate (TEOSPC) derivative of clindamycin phosphate (CLIP) as a chiral selector. A sol solution... |
|
|
Effects of antibiotic physicochemical properties on their release kinetics from biodegradable polymer microparticles.
Pharm. Res. 31(12) , 3379-89, (2014) This study investigated the effects of the physicochemical properties of antibiotics on the morphology, loading efficiency, size, release kinetics, and antibiotic efficacy of loaded poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microparticles (MPs) at different loa... |
|
|
Antibiotic prophylaxis for ED patients with simple hand lacerations: a feasibility randomized controlled trial.
Am. J. Emerg. Med. 32(7) , 768-71, (2014) The benefit of antibiotic prophylaxis for simple hand lacerations (lacerations that do not involve special structures) has not been adequately studied.To assess the feasibility of a randomized controlled trial to determine the role of antibiotic prophylaxis i... |
|
|
Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus obtained from Southeast of Iran (Kerman).
APMIS 122(5) , 405-11, (2014) Staphylococcus aureus infections, particularly infections caused by methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains, are emerging as a major public health problem. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of MRSA, antibiotic resistance profile and... |
|
|
D-Zone test for detection of inducible clindamycin resistance using SirScan paper disks and Rosco Neo-Sensitabs at 25 and 15 mm distances.
J. Med. Microbiol. 63(Pt 8) , 1052-4, (2014) Clindamycin is a possible antibiotic treatment of infections by Gram-positive cocci. However, its use can be limited by inducible clindamycin resistance. To screen for the presence of this type of resistance, the D-zone test is used. The aim of this study was... |
|
|
Topical antibiotic monotherapy prescribing practices in acne vulgaris.
J. Dermatolog. Treat. 25(2) , 97-9, (2014) The aim of this study is to evaluate the frequency of dosing topical antibiotics as monotherapy in the treatment of acne vulgaris, and physician specialty prescribing these medications.This study is a retrospective review of all visits with a sole diagnosis o... |