| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
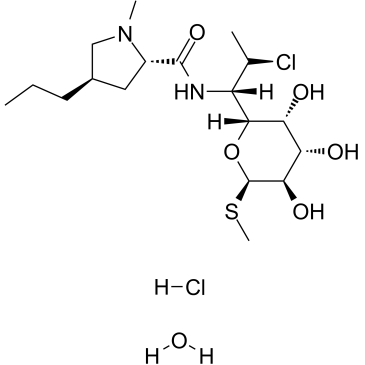 |
clindamycin hydrochloride
CAS:58207-19-5 |
|
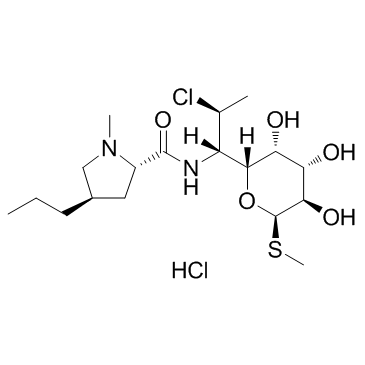 |
Clindamycin Hydrochloride
CAS:21462-39-5 |
|
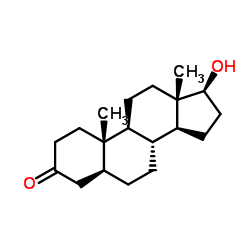 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
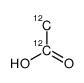 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
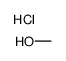 |
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE ~1.25 M IN METHANOL, 250 ML
CAS:132228-87-6 |