clindamycin hydrochloride
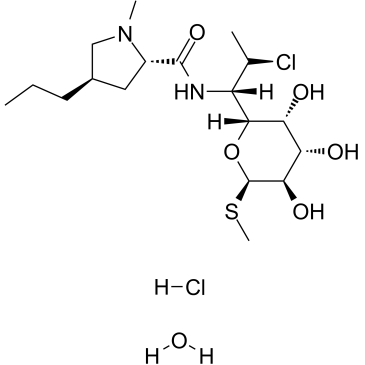
clindamycin hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | clindamycin hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58207-19-5 | Molecular Weight | 479.459 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 647ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H36Cl2N2O6S | Melting Point | 143ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 345.1ºC | |
Use of clindamycin hydrochlorideClindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate is an oral protein synthesis inhibitory agent that has the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla)[1]. |
| Name | Clindamycin Hydrochloride Monohydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate is an oral protein synthesis inhibitory agent that has the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 647ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 143ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H36Cl2N2O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 479.459 |
| Flash Point | 345.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 478.167114 |
| PSA | 136.79000 |
| LogP | 1.45600 |
| Index of Refraction | 143 ° (C=2, H2O) |
| InChIKey | KWMXKEGEOADCEQ-WNNJHRBUSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCC1CC(C(=O)NC(C(C)Cl)C2OC(SC)C(O)C(O)C2O)N(C)C1.Cl.O |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | GF2275000 |
| HS Code | 29419090 |
|
Performance characterization of a quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for 12 macrolide and lincosamide antibiotics in salmon, shrimp and tilapia.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 967 , 203-10, (2014) This paper describes an extension and performance characterization of a quantitative confirmatory multi-residue liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for residues of macrolide and lin... |
|
|
Development of a method to quantify clindamycin in vitreous humor of rabbits' eyes by UPLC-MS/MS: application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study and in vivo ocular biocompatibility evaluation.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 346-52, (2015) Ocular toxoplasmosis may result in uveitis in the posterior segment of the eye, leading to severe visual complications. Clindamycin-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) implants could be applied t... |
|
|
A biodegradable antibiotic-impregnated scaffold to prevent osteomyelitis in a contaminated in vivo bone defect model.
Eur. Cell. Mater. 27 , 332-49, (2014) Open fractures are at risk of serious infection and, if infected, require several surgical interventions and courses of systemic antibiotics. We investigated a new injectable formulation that simultan... |
| Methyl (5R)-5-[(1S,2S)-2-chloro-1-{[(4R)-1-methyl-4-propyl-L-prolyl]amino}propyl]-1-thio-β-L-arabinopyranoside hydrochloride hydrate |
| clindamycin hydrochloride hydrate |
| L-threo-α-D-galacto-Octopyranoside, methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-[[[(2S,4R)-1-methyl-4-propyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]carbonyl]amino]-1-thio-, hydrochloride, hydrate (1:1:1) |