3-Chlorobenzoic Acid
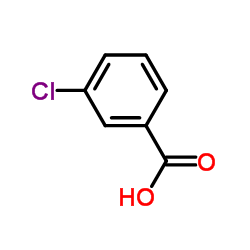
3-Chlorobenzoic Acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-Chlorobenzoic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 535-80-8 | Molecular Weight | 156.566 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 281.3±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5ClO2 | Melting Point | 153-157 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 123.9±19.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Molecular diversity in the bacterial community and the fluorescent pseudomonads group in natural and chlorobenzoate-stressed peat-forest soil.
Microbiol. Res. 158(1) , 47-54, (2003) Bacterial community shifts in a soil microcosm spiked with 3-chlorobenzoate or 2,5-dichlorobenzoate were monitored. The V6-V8 variable regions of soil bacterial 16S rRNA and rDNA were amplified and separated by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) ... |
|
|
Alginate beads as a storage, delivery and containment system for genetically modified PCB degrader and PCB biosensor derivatives of Pseudomonas fluorescens F113.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 110(5) , 1351-8, (2011) Pseudomonas fluorescens F113Rifpcb is a genetically engineered rhizosphere bacterium with the potential to degrade polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). F113Rifpcbgfp and F113L::1180gfp are biosensor strains capable of detecting PCB bioavailability and biodegrada... |
|
|
Amino acids in positions 48, 52, and 73 differentiate the substrate specificities of the highly homologous chlorocatechol 1,2-dioxygenases CbnA and TcbC.
J. Bacteriol. 187(15) , 5427-36, (2005) Chlorocatechol 1,2-dioxygenase (CCD) is the first-step enzyme of the chlorocatechol ortho-cleavage pathway, which plays a central role in the degradation of various chloroaromatic compounds. Two CCDs, CbnA from the 3-chlorobenzoate-degrader Ralstonia eutropha... |
|
|
Reactivity of toluate dioxygenase with substituted benzoates and dioxygen.
J. Bacteriol. 184(15) , 4096-103, (2002) Toluate dioxygenase (TADO) of Pseudomonas putida mt-2 catalyzes the dihydroxylation of a broad range of substituted benzoates. The two components of this enzyme were hyperexpressed and anaerobically purified. Reconstituted TADO had a specific activity of 3.8 ... |
|
|
Efficient turnover of chlorocatechols is essential for growth of Ralstonia eutropha JMP134(pJP4) in 3-chlorobenzoic acid.
J. Bacteriol. 185(5) , 1534-42, (2003) Ralstonia eutropha JMP134(pJP4) degrades 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CB) by using two not completely isofunctional, pJP4-encoded chlorocatechol degradation gene clusters, tfdC(I)D(I)E(I)F(I) and tfdD(II)C(II)E(II)F(II). Introduction of several copies of each gene clu... |
|
|
Effects of endogenous substrates on adaptation of anaerobic microbial communities to 3-chlorobenzoate.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72(1) , 449-56, (2006) Lengthy adaptation periods in laboratory studies evaluating the potential for contaminant biodegradation in natural or engineered environments may indicate that the native microbial communities are not metabolizing the contaminants in situ. In this study, we ... |
|
|
Genuine genetic redundancy in maleylacetate-reductase-encoding genes involved in degradation of haloaromatic compounds by Cupriavidus necator JMP134.
Microbiology 155(Pt 11) , 3641-51, (2009) Maleylacetate reductases (MAR) are required for biodegradation of several substituted aromatic compounds. To date, the functionality of two MAR-encoding genes (tfdF(I) and tfdF(II)) has been reported in Cupriavidus necator JMP134(pJP4), a known degrader of ar... |
|
|
The copy number of the catabolic plasmid pJP4 affects growth of Ralstonia eutropha JMP134 (pJP4) on 3-chlorobenzoate.
FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 212(1) , 95-100, (2002) Ralstonia eutropha JMP134 (pJP4) grows on 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CB) or 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate (2,4-D). The copy number of chlorocatechol genes has been observed to be important for allowing growth of bacterial strains on chloroaromatic compounds. Despite th... |
|
|
Vibrational investigation, molecular orbital studies and molecular electrostatic potential map analysis on 3-chlorobenzoic acid using hybrid computational calculations.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 84(1) , 210-20, (2011) The FT-IR and FT-Raman spectra of 3-chlorobenzoic acid (3CBA) are recorded in the liquid state. The fundamental vibrational frequencies, intensity of vibrational bands and the optimized geometrical parameters of the compound are evaluated using HF and DFT (LS... |
|
|
3-Chlorobenzoate is taken up by a chromosomally encoded transport system in Cupriavidus necator JMP134.
Microbiology 155(Pt 8) , 2757-65, (2009) Cupriavidus necator JMP134(pJP4) is able to grow on 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CB), a model chloroaromatic pollutant. Catabolism of 3-CB is achieved via the expression of the chromosomally encoded benABCD genes and the tfd genes from plasmid pJP4. Since passive diff... |