GD2-GANGLIOSIDE
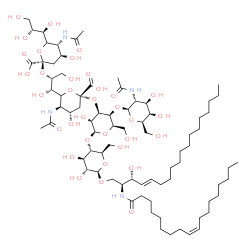
GD2-GANGLIOSIDE structure
|
Common Name | GD2-GANGLIOSIDE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 65988-71-8 | Molecular Weight | 1673.921 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1633.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C72H126N4O34 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 941.6±34.3 °C | |
|
Soluble Aβ oligomers are rapidly sequestered from brain ISF in vivo and bind GM1 ganglioside on cellular membranes.
Neuron 82(2) , 308-19, (2014) Soluble Aβ oligomers contribute importantly to synaptotoxicity in Alzheimer's disease, but their dynamics in vivo remain unclear. Here, we found that soluble Aβ oligomers were sequestered from brain interstitial fluid onto brain membranes much more rapidly th... |
|
|
Key role for myeloid cells: phase II results of anti-G(D2) antibody 3F8 plus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for chemoresistant osteomedullary neuroblastoma.
Int. J. Cancer 135(9) , 2199-205, (2014) Anti-G(D2) murine antibody 3F8 plus subcutaneously (sc) administered granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) was used against primary refractory neuroblastoma in metastatic osteomedullary sites. Large study size and long follow-up allowed as... |
|
|
Fenretinide sensitizes multidrug-resistant human neuroblastoma cells to antibody-independent and ch14.18-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity.
J. Mol. Med. 91(4) , 459-72, (2013) Neuroblastoma (NB) is the most common extracranial solid tumor in children. Combining passive immunotherapy with an antibody to the disialoganglioside GD2 (ch14.18/SP2/0) and cytokines with 13-cis-retinoic acid for post-myeloablative maintenance therapy incre... |
|
|
Validated detection of anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18/CHO in serum of neuroblastoma patients using anti-idiotype antibody ganglidiomab.
J. Immunol. Methods 398-399 , 51-9, (2013) Human/mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody (mAb) ch14.18 is directed against disialoganglioside GD2 and has demonstrated activity and efficacy in high-risk neuroblastoma (NB). For the purpose of industrial production, ch14.18 was manufactured in Chinese hamster... |
|
|
Uterine leiomyosarcoma diffusely express disialoganglioside GD2 and bind the therapeutic immunocytokine 14.18-IL2: implications for immunotherapy.
Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 61(7) , 1149-53, (2012) Uterine leiomyosarcoma comprises <1 % of uterine malignancies and is known for its clinically aggressive course. Extrapelvic recurrences are common and often lethal. No adjuvant therapies have been shown to significantly improve overall survival, highlighting... |
|
|
Enhancement of malignant properties of human osteosarcoma cells with disialyl gangliosides GD2/GD3.
Cancer Sci. 103(9) , 1656-64, (2012) The expression and implications of gangliosides in human osteosarcomas have not been systematically analyzed. In this study, we showed that gangliosides GD3 and GD2 are highly expressed in the majority of human osteosarcoma cell lines derived from oral cavity... |
|
|
An MRI-visible non-viral vector for targeted Bcl-2 siRNA delivery to neuroblastoma.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 7 , 3319-32, (2012) Polyethylene glycol-grafted polyethylenimine (PEG-g-PEI) which was functionalized with a neuroblastoma cell-specific ligand, the GD2 single chain antibody (scAb(GD2)), was synthesized in order to effectively deliver Bcl-2 siRNA into neuroblastoma cells. This ... |
|
|
Identification of tumoral glial precursor cells in neuroblastoma.
Cancer Lett. 312(1) , 73-81, (2011) Neuroblastic tumors (NBT) are composed by neuroblasts and Schwannian-like stroma. The origin of these two cell subtypes remains unclear. In this study, we describe, a neuroblastic-like subpopulation in neuroblastoma (NB) coexpressing GD2 and S100A6, neuroblas... |
|
|
Cancer vaccines and carbohydrate epitopes.
Vaccine 29(48) , 8802-26, (2011) Tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens (TACA) result from the aberrant glycosylation that is seen with transformation to a tumor cell. The carbohydrate antigens that have been found to be tumor-associated include the mucin related Tn, Sialyl Tn, and Thomsen-F... |
|
|
Trifunctional bispecific antibodies induce tumor-specific T cells and elicit a vaccination effect.
Cancer Res. 72(16) , 3958-66, (2012) A major goal of tumor immunotherapy is the induction of long-lasting systemic T-cell immunity. Bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) that lack the immunoglobulin Fc region confer T-cell-mediated killing of tumor cells but do not induce long-term memory. In contrast, ... |