Fenretinide sensitizes multidrug-resistant human neuroblastoma cells to antibody-independent and ch14.18-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity.
Anastasia Shibina, Diana Seidel, Srinivas S Somanchi, Dean A Lee, Alexander Stermann, Barry J Maurer, Holger N Lode, C Patrick Reynolds, Nicole Huebener
Index: J. Mol. Med. 91(4) , 459-72, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Neuroblastoma (NB) is the most common extracranial solid tumor in children. Combining passive immunotherapy with an antibody to the disialoganglioside GD2 (ch14.18/SP2/0) and cytokines with 13-cis-retinoic acid for post-myeloablative maintenance therapy increased survival in high-risk NB, but the overall prognosis for these children is still in need of improvement. Fenretinide (4-HPR) is a synthetic retinoid that has shown clinical activity in recurrent NB and is cytotoxic to a variety of cancer cells, in part via the accumulation of dihydroceramides, which are precursors of GD2. We investigated the effect of 4-HPR on CHO-derived, ch14.18-mediated anti-NB effector functions, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent and antibody-independent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC and AICC, respectively). Here, we demonstrate for the first time that pretreatment of fenretinide-resistant NB cells with 4-HPR significantly enhanced ch14.18/CHO-mediated CDC and ADCC and AICC by both human natural killer cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Treatment with 4-HPR increased GD2 and death receptor (DR) expression in resistant NB cells and induced an enhanced granzyme B and perforin production by effector cells. Blocking of ganglioside synthesis with a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor abrogated the increased ADCC response but had no effect on the AICC, indicating that GD2 induced by 4-HPR mediates the sensitization of NB cells for ADCC. We also showed that 4-HPR induced increased GD2 and DR expression in a resistant NB xenograft model that was associated with an increased ADCC and AICC response using explanted tumor target cells from 4-HPR-treated mice. In summary, these findings provide an important baseline for the combination of 4-HPR and passive immunotherapy with ch14.18/CHO in future clinical trials for high-risk NB patients.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
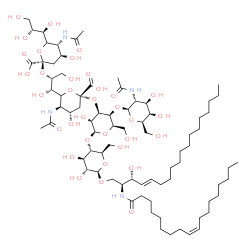 |
GD2-GANGLIOSIDE
CAS:65988-71-8 |
C72H126N4O34 |
|
Soluble Aβ oligomers are rapidly sequestered from brain ISF ...
2014-04-16 [Neuron 82(2) , 308-19, (2014)] |
|
Key role for myeloid cells: phase II results of anti-G(D2) a...
2014-11-01 [Int. J. Cancer 135(9) , 2199-205, (2014)] |
|
Validated detection of anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18/CHO in seru...
2013-12-15 [J. Immunol. Methods 398-399 , 51-9, (2013)] |
|
Uterine leiomyosarcoma diffusely express disialoganglioside ...
2012-07-01 [Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 61(7) , 1149-53, (2012)] |
|
Enhancement of malignant properties of human osteosarcoma ce...
2012-09-01 [Cancer Sci. 103(9) , 1656-64, (2012)] |