Tartaric acid
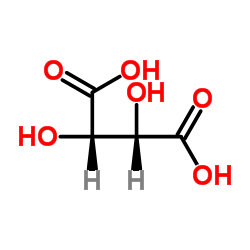
Tartaric acid structure
|
Common Name | Tartaric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 87-69-4 | Molecular Weight | 150.087 | |
| Density | 1.76 | Boiling Point | 399.3±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O6 | Melting Point | 170-172 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 210 ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Leishmania amazonensis: characterization of an ecto-pyrophosphatase activity.
Exp. Parasitol. 137 , 8-13, (2014) Several ecto-enzymatic activities have been described in the plasma membrane of the protozoan Leishmania amazonensis, which is the major etiological agent of diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis in South America. These enzymes, including ecto-phosphatases, contrib... |
|
|
Enamel protection from acid challenge--benefits of marketed fluoride dentifrices.
J. Clin. Dent. 24(1) , 25-30, (2013) To determine the ability of various marketed dentifrices containing stabilized stannous fluoride (SnF2), sodium fluoride (NaF), or sodium monofluorophosphate (SMFP) to protect enamel against the earliest stages of erosive dietary acid damage using an in vitro... |
|
|
The EpiOcular Eye Irritation Test (EIT) for hazard identification and labelling of eye irritating chemicals: protocol optimisation for solid materials and the results after extended shipment.
Altern. Lab. Anim. 43 , 101-27, (2015) The 7th Amendment to the EU Cosmetics Directive and the EU REACH Regulation have reinforced the need for in vitro ocular test methods. Validated in vitro ocular toxicity tests that can predict the human response to chemicals, cosmetics and other consumer prod... |
|
|
HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue) , D603-10, (2009) The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB, http://www.hmdb.ca) is a richly annotated resource that is designed to address the broad needs of biochemists, clinical chemists, physicians, medical geneticists, nutritionists and members of the metabolomics community. Si... |
|
|
Prediction of skeletal muscle and fat mass in patients with advanced cancer using a metabolomic approach.
J. Nutr. 142(1) , 14-21, (2012) Urine and plasma metabolites originate from endogenous metabolic pathways in different organs and exogenous sources (diet). Urine and plasma were obtained from advanced cancer patients and investigated to determine if variations in lean and fat mass, dietary ... |
|
|
Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.
Nature 457(7231) , 910-4, (2009) Multiple, complex molecular events characterize cancer development and progression. Deciphering the molecular networks that distinguish organ-confined disease from metastatic disease may lead to the identification of critical biomarkers for cancer invasion an... |
|
|
Volatile Compounds from Grape Skin, Juice and Wine from Five Interspecific Hybrid Grape Cultivars Grown in Québec (Canada) for Wine Production.
Molecules 20 , 10980-1016, (2015) Developed from crosses between Vitis vinifera and North American Vitis species, interspecific hybrid grape varieties are becoming economically significant in northern areas, where they are now extensively grown for wine production. However, the varietal diffe... |
|
|
Quantitative analysis for organic acids in biological samples: batch isolation followed by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis.
Clin. Chem. 35(4) , 587-95, (1989) This new method for qualitative and quantitative determination of organic acids, aldehydes, and ketones in biological samples is effective for use with urine, plasma, and amniotic fluid, and it requires no deproteinization. Isolation by batch-wise liquid part... |
|
|
Untargeted metabolomic analysis using liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for non-volatile profiling of wines.
Anal. Chim. Acta 858 , 32-41, (2015) The current study presents a method for comprehensive untargeted metabolomic fingerprinting of the non-volatile profile of the Graciano Vitis vinifera wine variety, using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-Q... |
|
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine.
Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequent cause of kidney failure; however, urinary biomarkers for the disease are lacking. In a step towards identifying such markers, we used multidimensional-multinuclear nuclear magnetic resonance (... |