Astaxanthin
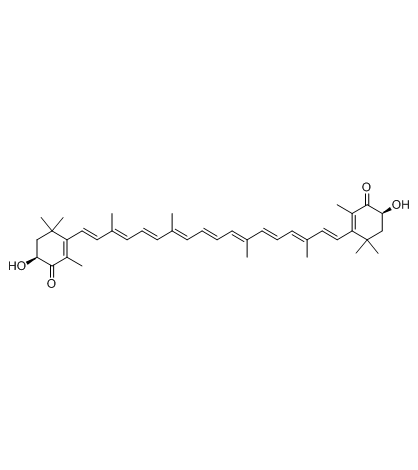
Astaxanthin structure
|
Common Name | Astaxanthin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 472-61-7 | Molecular Weight | 596.839 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 774.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H52O4 | Melting Point | 215-216ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 435.8±29.4 °C | |
|
Effect of AST on age-associated changes of vocal folds in a rat model.
Laryngoscope 124(10) , E411-7, (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are associated with aging. Astaxanthin (AST) is a strong antioxidant and has been reported to prevent various ROS-induced diseases. In the current study, we investigated the effect of AST on age-associated histological and mRNA c... |
|
|
Effect of dietary formic acid and astaxanthin on the survival and growth of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and their resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus.
Springerplus 4 , 440, (2015) A 90-day feeding trial was conducted to evaluate the effects of formic acid (FA) and astaxanthin (AX) on growth, survival, immune parameters, and tolerance to Vibrio infection in Pacific white shrimp. The study was divided into two experiments. In experiment ... |
|
|
Morphological, molecular, and biochemical characterization of astaxanthin-producing green microalga Haematococcus sp. KORDI03 (Haematococcaceae, Chlorophyta) isolated from Korea.
J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25(2) , 238-46, (2015) A unicellular red microalga was isolated from environmental freshwater in Korea, and its morphological, molecular, and biochemical properties were characterized. Morphological analysis revealed that the isolate was a unicellular biflagellated green microalga ... |
|
|
Characterization of Shrimp Oil from Pandalus borealis by High Performance Liquid Chromatography and High Resolution Mass Spectrometry.
Mar. Drugs 13 , 3849-76, (2015) Northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis) oil, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, was recovered from the cooking water of shrimp processing facilities. The oil contains significant amounts of omega-3 fatty acids in triglyceride form, along with substantial long-... |
|
|
Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 17192, (2015) Hepatic insulin resistance and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) could be caused by excessive hepatic lipid accumulation and peroxidation. Vitamin E has become a standard treatment for NASH. However, astaxanthin, an antioxidant carotenoid, inhibits lipid pe... |
|
|
Fatty acids attached to all-trans-astaxanthin alter its cis-trans equilibrium, and consequently its stability, upon light-accelerated autoxidation.
Food Chem. 194 , 1108-15, (2015) Fatty acid esterification, common in naturally occurring astaxanthin, has been suggested to influence both colour stability and degradation of all-trans-astaxanthin. Therefore, astaxanthin stability was studied as influenced by monoesterification and diesteri... |
|
|
Determination of Other Related Carotenoids Substances in Astaxanthin Crystals Extracted from Adonis amurensis.
J. Oleo Sci. 64 , 751-9, (2015) Astaxanthin is a kind of important carotenoids with powerful antioxidation capacity and other health functions. Extracting from Adonis amurensis is a promising way to obtain natural astaxanthin. However, how to ensure the high purity and to investigate relate... |
|
|
Astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis Prevents Oxidative Stress on Human Endothelial Cells without Toxicity.
Mar. Drugs 13 , 2857-74, (2015) Astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant, is a good candidate for the prevention of intracellular oxidative stress. The aim of the study was to compare the antioxidant activity of astaxanthin present in two natural extracts from Haematococcus pluvialis, a microalg... |
|
|
Protective effects of astaxanthin on ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis by the JNK/p-JNK pathway-mediated inhibition of autophagy and apoptosis.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0120440, (2015) Astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant, exhibits a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidant, atherosclerosis and antitumor activities. However, its effect on concanavalin A (ConA)-induced autoimmune hepatitis remains unclear. The aim of this stud... |
|
|
An immune-modulating diet increases the regulatory T cells and reduces T helper 1 inflammatory response in Leishmaniosis affected dogs treated with standard therapy.
BMC Vet. Res. 11 , 295, (2015) Clinical appearance and evolution of Canine Leishmaniosis (CL) are the consequence of complex interactions between the parasite and the genetic and immunological backgrounds. We investigated the effect of an immune-modulating diet in CL. Dogs were treated wit... |