ALLM
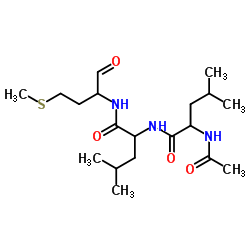
ALLM structure
|
Common Name | ALLM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 136632-32-1 | Molecular Weight | 401.564 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 676.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H35N3O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 362.9±31.5 °C | |
|
Compartmentalization of the chick cerebellar cortex based on the link between the striped expression pattern of aldolase C and the topographic olivocerebellar projection.
J. Comp. Neurol. 523 , 1886-912, (2015) The avian cerebellum is organized into multiple longitudinal stripes defined by expression profiles of aldolase C (zebrin II) in Purkinje cells. The relationship between the aldolase C striped pattern and the olivocerebellar projection pattern is crucial in u... |
|
|
Targeting microparticle biogenesis: a novel approach to the circumvention of cancer multidrug resistance.
Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 15 , 205-14, (2015) Microparticles (MPs) are released from most eukaryotic cells after the vesiculation of the plasma membrane and serve as vectors of long and short-range signaling. MPs derived from multidrug resistant (MDR) cancer cells carry molecular components of the donor ... |
|
|
Increased μ-Calpain Activity in Blasts of Common B-Precursor Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Correlates with Their Lower Susceptibility to Apoptosis.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0136615, (2015) Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) blasts are characterized by inhibited apoptosis promoting fast disease progress. It is known that in chronic lymphocytic and acute myeloid leukemias the reduced apoptosis is strongly related with the activity of ca... |
|
|
Novel targets for Huntington's disease in an mTOR-independent autophagy pathway.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 4 , 295-305, (2008) Autophagy is a major clearance route for intracellular aggregate-prone proteins causing diseases such as Huntington's disease. Autophagy induction with the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin accelerates clearance of these toxic substrates. As rapamycin has nontrivial s... |
|
|
The cyclin-dependent kinase activator, Spy1A, is targeted for degradation by the ubiquitin ligase NEDD4.
J. Bacteriol. 284 , 2617-27, (2009) Spy1A is a cyclin-like protein required for progression through the G(1)/S phase of the cell cycle. Elevated Spy1A protein levels have been implicated in tumorigenesis and are attributed to overriding the DNA damage response and enhancing cell proliferation. ... |
|
|
The role of MAP1A light chain 2 in synaptic surface retention of Cav2.2 channels in hippocampal neurons.
J. Neurosci. 28(44) , 11333-46, (2008) Ca(v)2.2 channels are localized at nerve terminals where they play a critical role in neurotransmission. However, the determinant that controls surface retention of these channels has not been identified. Here, we report that presynaptic surface localization ... |
|
|
Synthesis and proteasome inhibition of glycyrrhetinic acid derivatives.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 6696-6701, (2008) This study discovered that glycyrrhetinic acid inhibited the human 20S proteasome at 22.3microM. Esterification of the C-3 hydroxyl group on glycyrrhetinic acid with various carboxylic acid reagents yielded a series of analogs with marked improved potency. Am... |
|
|
Verapamil but not calpain or creatine alters arsenate-induced cardiac cell death.
Toxicol. Ind. Health 25 , 169-76, (2009) The objective of this study was to examine the potential of arsenate to induce cardiomyocyte cell death and to explore the cellular mechanisms of arsenate toxicity. Isolated cardiomyocytes in culture from embryonic chick hearts were treated with a pentavalent... |
|
|
Ongoing DNA synthesis in the rat cerebral cortex is regulated by a proteolytic pathway independent of the proteasome and calpains.
Invest. New Drugs 28 , 242-50, (2010) By using mini-units of tissue and protease inhibitors in short term incubation (0-180 min), we studied the role of proteolysis for ongoing DNA replication in the developing rat cerebral cortex. The protease inhibitors TLCK, TPCK, PMSF, MG-132 and PSI markedly... |
|
|
Very low levels of methylmercury induce cell death of cultured rat cerebellar neurons via calpain activation.
Toxicology 213 , 97-106, (2005) Methylmercury, an environmental neurotoxicant, induces the apoptotic death of cerebellar granule cells in vitro at a low concentration. To further understand the mechanism of cell death, we used a rat cerebellar granule cell culture system to investigate whet... |