Shellac
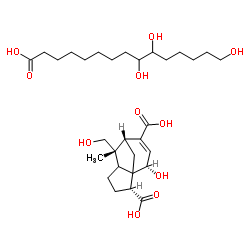
Shellac structure
|
Common Name | Shellac | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9000-59-3 | Molecular Weight | N/A | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H50O11 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Emergent and unusual allergens in cosmetics.
Dermatitis 21(3) , 127-37, (2010) Allergic contact dermatitis from cosmetics is a common problem that is occasionally caused by new or rare allergens. When a patient has a positive patch test to a cosmetic product but to none of the common or commercially available allergens, it is important ... |
|
|
[Bio-based pharmaceutical polymers, possibility of their chemical modification and the applicability of modified polymers].
Acta Pharm. Hung. 82(4) , 138-54, (2012) Different types of polymers are widely used in biomedical, pharmaceutical and cosmetic purposes. Their applications are curbed, if the polymers can not break down by the body or if the polymer itself is harmful or decompose to harmful material. Authors provid... |
|
|
Effect of solid content and composition of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-lipid edible coatings on physico-chemical and nutritional quality of 'Oronules' mandarins.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 92(4) , 794-802, (2012) Citrus fruit represent an important source of vitamin C, as well as other bioactive compounds. Edible coatings have the potential to extend shelf life of citrus by providing a semi-permeable barrier to water and gases, which depends on coating composition, so... |
|
|
Development of shellac-coated sustained release pellet formulations.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 42(4) , 400-5, (2011) Shellac is an important coating material for food products. Since the introduction of aqueous ammoniacal solutions it also regained importance for pharmaceutical applications. Because of the comparatively high dissolution pH of this material, further additive... |
|
|
Fabrication of pseudo-ceramide-based lipid microparticles for recovery of skin barrier function.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 94 , 236-41, (2012) The recovery of skin barrier functions was investigated with pseudo-ceramide-based lipid microparticles. The microparticles were prepared by using a fluid bed technique where lipid components (a pseudo-ceramide, cholesterol and a fatty acid) were coated on a ... |
|
|
Characterizing permeability and stability of microcapsules for controlled drug delivery by dynamic NMR microscopy.
J. Magn. Reson. 221 , 11-8, (2012) Microscopic capsules made from polysaccharides are used as carriers for drugs and food additives. Here, we use NMR microscopy to assess the permeability of capsule membranes and their stability under different environmental conditions. The results allow us to... |
|
|
Novel multifunctional micro-ampoules for structuring and encapsulation.
ChemPhysChem 10(15) , 2599-602, (2009)
|
|
|
Investigation of various shellac grades: additional analysis for identity.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 35(6) , 694-703, (2009) A number of different grades of shellac are commercially available and most of them are known only as generic shellac and are not further differentiated. The investigated grades of shellac in this study are based on different insect strains, host trees, refin... |
|
|
Development and in vitro evaluation of ketoprofen extended release pellets using powder layering technique in a rotary centrifugal granulator.
Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 14(2) , 138-45, (2011) Powder layering technique was evaluated using laboratory scale centrifugal granulator instrument to prepare extended release pellet dosage form of ketoprofen. Ethyl cellulose and shellac polymers were used for drug layering and extended release coating in the... |
|
|
Investigation of drug release from pellets coated with different shellac types.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 37(2) , 193-200, (2011) Even though most commercially available shellac types meet the specifications of the pharmacopoeias, their physicochemical properties and thus drug release may vary considerably. So far a comparison of drug release from dosage forms coated with different shel... |