poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
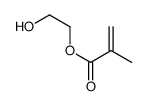
poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) structure
|
Common Name | poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 25249-16-5 | Molecular Weight | 130.14200 | |
| Density | 1.054g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 189ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 97.2ºC | |
|
Increased protein sorption in poly(acrylic acid)-containing films through incorporation of comb-like polymers and film adsorption at low pH and high ionic strength.
Langmuir 29(9) , 2946-54, (2013) In principle, incorporation of comb-like block copolymers in multilayer polyelectrolyte films can both increase film thickness relative to coatings containing linear polymers and provide more swollen films for increased sorption of proteins. In the absence of... |
|
|
Hydrogels that mimic developmentally relevant matrix and N-cadherin interactions enhance MSC chondrogenesis.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(25) , 10117-22, (2013) Methacrylated hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels provide a backbone polymer with which mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can interact through several cell surface receptors that are expressed by MSCs, including CD44 and CD168. Previous studies showed that this 3D hyd... |
|
|
S100A7 acts as a dual regulator in promoting proliferation and suppressing squamous differentiation through GATA-3/caspase-14 pathway in A431 cells.
Exp. Dermatol. 24 , 342-8, (2015) S100A7 is expressed in many squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs), such as SCC of the skin, and well-differentiated SCC always displays stronger staining of this protein. A431 cells, an epidermal cancer cell line, were selected as a cell model to investigate the ro... |
|
|
Characterization and cellular interaction of fluorescent-labeled PHEMA nanoparticles.
Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 41(2) , 78-84, (2013) The aim of this study is to label the cells with polymeric nanoparticles properly and efficiently. For this purpose, acridine orange (AO)-loaded poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) nanoparticles were synthesized by miniemulsion polymerization. PHEMA nan... |
|
|
Isolation of human adult olfactory sphere cells as a cell source of neural progenitors.
Stem Cell Res. 15 , 23-9, (2015) Olfactory stem cells are generated from olfactory mucosa. Various culture conditions generate olfactory stem cells that differ according to species and developmental stage and have different progenitor or stem cell characteristics. Olfactory spheres (OSs) are... |
|
|
Changes in endometrial ezrin and cytokeratin 18 expression during bovine implantation and in caruncular endometrial spheroids in vitro.
Placenta 36 , 821-31, (2015) The feto-maternal interface during bovine implantation was studied in vivo and using three-dimensional bovine endometrial (BCECph) and trophoblast spheroids (CCS), each with underlying fibroblasts.The expression of ezrin and cytokeratin 18 (CK18) was analyzed... |
|
|
Targeting tumor-initiating cells: eliminating anabolic cancer stem cells with inhibitors of protein synthesis or by mimicking caloric restriction.
Oncotarget 6(7) , 4585-601, (2015) We have used an unbiased proteomic profiling strategy to identify new potential therapeutic targets in tumor-initiating cells (TICs), a.k.a., cancer stem cells (CSCs). Towards this end, the proteomes of mammospheres from two breast cancer cell lines were dire... |
|
|
Preparation and use of poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) cryogels containing L-histidine for β-casein adsorption.
J. Food Sci. 78(2) , E238-43, (2013) The objective of this study was to determine β-casein adsorption by using supermacroporous poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-N-methacryloyl-(l)-histidine methyl ester) [p(HEMA-MAH)] cryogel. β-Casein adsorption properties of p(HEMA-MAH) cryogel were studied fo... |
|
|
Doxycycline down-regulates DNA-PK and radiosensitizes tumor initiating cells: Implications for more effective radiation therapy.
Oncotarget 6 , 14005-25, (2015) DNA-PK is an enzyme that is required for proper DNA-repair and is thought to confer radio-resistance in cancer cells. As a consequence, it is a high-profile validated target for new pharmaceutical development. However, no FDA-approved DNA-PK inhibitors have e... |
|
|
Mitochondrial biogenesis is required for the anchorage-independent survival and propagation of stem-like cancer cells.
Oncotarget 6 , 14777-95, (2015) Here, we show that new mitochondrial biogenesis is required for the anchorage independent survival and propagation of cancer stem-like cells (CSCs). More specifically, we used the drug XCT790 as an investigational tool, as it functions as a specific inhibitor... |