Pyridoxine
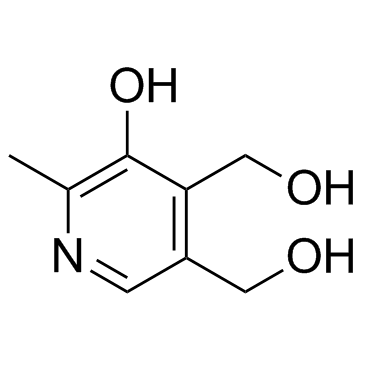
Pyridoxine structure
|
Common Name | Pyridoxine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 65-23-6 | Molecular Weight | 169.178 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 491.9±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11NO3 | Melting Point | 159-162ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 251.3±27.3 °C | |
|
Tissue vitamin concentrations are maintained constant by changing the urinary excretion rate of vitamins in rats' restricted food intake.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 78(12) , 2102-9, (2014) We previously reported that mild food restriction induces a reduction in tryptophan-nicotinamide conversion, which helps to explain why death secondary to pellagra is pandemic during the hungry season. In this study, we investigated the levels of B-group vita... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Nanosized silver (II) pyridoxine complex to cause greater inflammatory response and less cytotoxicity to RAW264.7 macrophage cells.
Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10 , 140, (2015) With advancements in nanotechnology, silver has been engineered into a nanometre size and has attracted great research interest for use in the treatment of wounds. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have emerged as a potential alternative to conventional antibiotic... |
|
|
Plant regeneration and biochemical accumulation of hydroxybenzoic and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in Hypoxis hemerocallidea organ and callus cultures.
Plant Sci. 227 , 157-64, (2014) Micropropagation of Hypoxis hemerocallidea Fisch. and C.A. Mey was used as a model system to study the influence of cytokinins (CKs) on plant regeneration and biochemical accumulation of hydroxybenzoic and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in organ and callus ... |
|
|
SPE-NMR metabolite sub-profiling of urine.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 404(8) , 2349-61, (2012) NMR-based metabolite profiling of urine is a fast and reproducible method for detection of numerous metabolites with diverse chemical properties. However, signal overlap in the (1)H NMR profiles of human urine may hamper quantification and identification of m... |
|
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine.
Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequent cause of kidney failure; however, urinary biomarkers for the disease are lacking. In a step towards identifying such markers, we used multidimensional-multinuclear nuclear magnetic resonance (... |
|
|
Digoxin and adenosine triphosphate enhance the functional properties of tissue-engineered cartilage.
Tissue Eng. Part A 21(5-6) , 884-94, (2015) Toward developing engineered cartilage for the treatment of cartilage defects, achieving relevant functional properties before implantation remains a significant challenge. Various chemical and mechanical stimuli have been used to enhance the functional prope... |