Propyl Ether
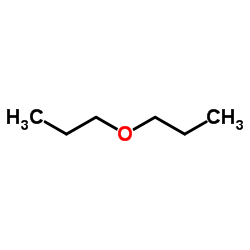
Propyl Ether structure
|
Common Name | Propyl Ether | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 111-43-3 | Molecular Weight | 102.175 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 90.2±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H14O | Melting Point | -123 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 4.4±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Anomalously slow proton transport of a water molecule.
J. Phys. Chem. B 115(19) , 6023-31, (2011) Unusually low proton-transporting ability of a water molecule has been observed in the excited-state proton transfer (ESPT) of a 7-azaindole (7AI) molecule complexed cyclically with a water molecule in diethyl ether and dipropyl ether. In contrast with ultraf... |
|
|
The unusually large Plasmodium telomerase reverse-transcriptase localizes in a discrete compartment associated with the nucleolus.
Nucleic Acids Res. 33 , 1111-22, (2005) Telomerase replicates chromosome ends, a function necessary for maintaining genome integrity. We have identified the gene that encodes the catalytic reverse transcriptase (RT) component of this enzyme in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum (PfTERT) as ... |
|
|
A Novel Docetaxel-Loaded Poly (ε-Caprolactone)/Pluronic F68 Nanoparticle Overcoming Multidrug Resistance for Breast Cancer Treatment.
Nanoscale Res. Lett. 4 , 1530-9, (2011) Multidrug resistance (MDR) in tumor cells is a significant obstacle to the success of chemotherapy in many cancers. The purpose of this research is to test the possibility of docetaxel-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone)/Pluronic F68 (PCL/Pluronic F68) nanoparticles... |
|
|
Propyl ether. II. Pulmonary irritation and anaesthesia.
Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 56(2) , 165-75, (1985) After cessation of the sensory irritation response, described in part one (Nielsen et al. 1985), a mixed response due to pulmonary irritation and anaesthesia appeared, resulting a decrease in respiratory rate and tidal volume. The corresponding thresholds wer... |
|
|
Sites for uptake of inhaled vapors in beagle dogs.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 109(2) , 263-75, (1991) The site of uptake of inhaled vapors profoundly influences which respiratory tract tissues receive the highest doses. How the site of uptake depends on the physicochemical properties of inhaled vapors has been the subject of experiment and speculation for dec... |
|
|
Synthesis of poly(propyl ether imine) dendrimers and evaluation of their cytotoxic properties.
J. Org. Chem. 68(25) , 9694-704, (2003) In this paper, we report the synthesis of several poly(propyl ether imine) dendrons and dendrimers. These dendrons and dendrimers were constructed by involving an ether as the linker component and an imine as the branching component. The divergent syntheses o... |
|
|
Propyl ether. I. Interaction with the sensory irritant receptor.
Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 56(2) , 158-64, (1985) The sensory irritating response of propyl ether, measured as a decrease in respiratory rate in mice, faded within one minute. The threshold was 620 p.p.m., calculated from the concentration-response curve, which had a low slope. The sensory irritating level d... |
|
|
Dendrimer building toolkit: model building and characterization of various dendrimer architectures.
J. Comput. Chem. 33(25) , 1997-2011, (2012) We have developed a graphical user interface based dendrimer builder toolkit (DBT) which can be used to generate the dendrimer configuration of desired generation for various dendrimer architectures. The validation of structures generated by this tool was car... |
|
|
Sustained release of protein from poly(ethylene glycol) incorporated amphiphilic comb like polymers.
Int. J. Pharm. 326(1-2) , 119-27, (2006) Amphiphilic comb like macromonomer containing hydrophilic poly(ethylene glycol) groups covalently linked to poly(hydromethyl siloxane) (PHMS) were prepared by hydrosilylation reaction. The epoxy reacting sites were introduced to this amphiphilic system by the... |
|
|
Interaction of single-walled carbon nanotubes with poly(propyl ether imine) dendrimers.
J. Chem. Phys. 134(10) , 104507, (2011) We study the complexation of nontoxic, native poly(propyl ether imine) dendrimers with single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). The interaction was monitored by measuring the quenching of inherent fluorescence of the dendrimer. The dendrimer-nanotube binding a... |