N,N'-Diacetylchitobiose
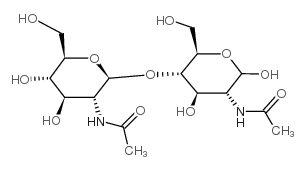
N,N'-Diacetylchitobiose structure
|
Common Name | N,N'-Diacetylchitobiose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 35061-50-8 | Molecular Weight | 424.40000 | |
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 927.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H28N2O11 | Melting Point | 245-247 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 514.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Slow Off-rates and Strong Product Binding Are Required for Processivity and Efficient Degradation of Recalcitrant Chitin by Family 18 Chitinases.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 29074-85, (2015) Processive glycoside hydrolases are the key components of enzymatic machineries that decompose recalcitrant polysaccharides, such as chitin and cellulose. The intrinsic processivity (P(Intr)) of cellulases has been shown to be governed by the rate constant of... |
|
|
Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(18) , 7182-7, (2013) The global demand for food could double in another 40 y owing to growth in the population and food consumption per capita. To meet the world's future food and sustainability needs for biofuels and renewable materials, the production of starch-rich cereals and... |
|
|
Chitinase III in Euphorbia characias latex: Purification and characterization.
Protein Expr. Purif. 116 , 152-8, (2015) This paper deals with the purification of a class III endochitinase from Euphorbia characias latex. Described purification method includes an effective novel separation step using magnetic chitin particles. Application of magnetic affinity adsorbent noticeabl... |
|
|
A LysR-Type Transcriptional Regulator, RovM, Senses Nutritional Cues Suggesting that It Is Involved in Metabolic Adaptation of Yersinia pestis to the Flea Gut.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0137508, (2015) Yersinia pestis has evolved as a clonal variant of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis to cause flea-borne biofilm-mediated transmission of the bubonic plague. The LysR-type transcriptional regulator, RovM, is highly induced only during Y. pestis infection of the fle... |
|
|
An ammonium sulfate sensitive chitinase from Streptomyces sp. CS501.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 37(12) , 1522-9, (2014) A chitinase from Streptomyces sp. CS501 was isolated from the Korean soil sample, purified by single-step chromatography, and biochemically characterized. The extracellular chitinase (Ch501) was purified to 4.60 fold with yield of 28.74 % using Sepharose Cl-6... |
|
|
Chitobiose phosphorylase from Vibrio proteolyticus, a member of glycosyl transferase family 36, has a clan GH-L-like (alpha/alpha)(6) barrel fold.
Structure 12 , 937-947, (2004) Vibrio proteolyticus chitobiose phosphorylase (ChBP) belongs to glycosyl transferase family 36 (GT-36), and catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of chitobiose into alpha-GlcNAc-1-phosphate and GlcNAc with inversion of the anomeric configuration. As the fir... |
|
|
Synthesis and X-ray crystallographic investigation of N-(β-D-glycosyl)butanamides derived from GlcNAc and chitobiose as analogs of the conserved chitobiosylasparagine linkage of N-glycoproteins.
Carbohydr. Res. 380 , 37-44, (2013) The linkage region, GlcNAcβAsn, is conserved in all eukaryotic N-glycoproteins. As a logical extension of a research endeavor aimed at understanding the structural significance of GlcNAc and Asn as the linkage region constituents, the newer analogs GlcNAcβNHB... |
|
|
Modulation of acceptor specificity of Ruminococcus albus cellobiose phosphorylase through site-directed mutagenesis.
Carbohydr. Res. 379 , 21-5, (2013) Cellobiose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.20, CBP) catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of cellobiose to α-D-glucose 1-phosphate (Glc1P) and d-glucose. Cys485, Tyr648, and Glu653 of CBP from Ruminococcus albus, situated at the +1 subsite, were mutated to modulate... |
|
|
The beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases NAG1 and NAG2 are essential for growth of Trichoderma atroviride on chitin.
FEBS J. 276 , 5137-5148, (2009) The chitinolytic enzyme machinery of fungi consists of chitinases and beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases. These enzymes are important during the fungal life cycle for degradation of exogenous chitin, which is the second most abundant biopolymer, as well as fungal ... |
|
|
The chitobiose transporter, chbC, is required for chitin utilization in Borrelia burgdorferi.
BMC Microbiol. 10 , 21, (2010) The bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, is a limited-genome organism that must obtain many of its biochemical building blocks, including N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), from its tick or vertebrate host. GlcNAc can be imported in... |