Fluorescein-5-maleimide
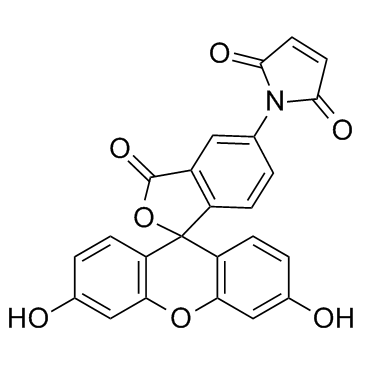
Fluorescein-5-maleimide structure
|
Common Name | Fluorescein-5-maleimide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75350-46-8 | Molecular Weight | 427.362 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 769.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H13NO7 | Melting Point | >275ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 418.9±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Analysis of tryptophan residues in the staphylococcal multidrug transporter QacA reveals long-distance functional associations of residues on opposite sides of the membrane.
J. Bacteriol. 190(7) , 2441-9, (2008) Tryptophan residues can possess a multitude of functions within a multidrug transport protein, e.g., mediating interactions with substrates or distal parts of the protein, or fulfilling a structural requirement, such as guiding the depth of membrane insertion... |
|
|
Fluorophore-labeled beta-lactamase as a biosensor for beta-lactam antibiotics: a study of the biosensing process.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(20) , 6351-61, (2008) The fluorescein-labeled E166C mutant of the PenPC beta-lactamase (E166Cf) represents a successful model in the construction of "switch-on" fluorescent biosensors from nonallosteric proteins (Chan P.-H. et al.; J. Am Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 4074). This paper fo... |
|
|
Accurate high-throughput structure mapping and prediction with transition metal ion FRET.
Structure 21(1) , 9-19, (2013) Mapping the landscape of a protein's conformational space is essential to understanding its functions and regulation. The limitations of many structural methods have made this process challenging for most proteins. Here, we report that transition metal ion FR... |
|
|
Cytosolic region of TM6 in P-glycoprotein: topographical analysis and functional perturbation by site directed labeling.
Biochemistry 47(12) , 3615-24, (2008) Reduced intracellular drug accumulation due to the activity of the drug efflux pump ABC (B1) is a major mechanism in the resistance of cancer cells to chemotherapy. ABC (B1) is a poly specific transporter, and the molecular mechanism of its complex translocat... |
|
|
Fluoresceination of FepA during colicin B killing: effects of temperature, toxin and TonB.
Mol. Microbiol. 72(5) , 1171-80, (2009) We studied the reactivity of 35 genetically engineered Cys sulphydryl groups at different locations in Escherichia coli FepA. Modification of surface loop residues by fluorescein maleimide (FM) was strongly temperature-dependent in vivo, whereas reactivity at... |
|
|
Conformation-dependent accessibility of Cys-136 and Cys-155 of the mitochondrial rat carnitine/acylcarnitine carrier to membrane-impermeable SH reagents.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1767(11) , 1331-9, (2007) During substrate translocation mitochondrial carriers cycle between the cytoplasmic-state (c-state) with substrate-binding site open to the intermembrane space and matrix-state (m-state) with the binding site open to the mitochondrial matrix. Here, the access... |
|
|
Fluorometric measurements of intermolecular distances between the alpha- and beta-subunits of the Na+/K+-ATPase.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(47) , 36338-46, (2006) The Na+/K+-ATPase maintains the physiological Na+ and K+ gradients across the plasma membrane in most animal cells. The functional unit of the ion pump is comprised of two mandatory subunits including the alpha-subunit, which mediates ATP hydrolysis and ion t... |
|
|
Transmembrane domain II of the Na+/proline transporter PutP of Escherichia coli forms part of a conformationally flexible, cytoplasmic exposed aqueous cavity within the membrane.
J. Biol. Chem. 278(44) , 42942-9, (2003) The Na+/proline transporter PutP of Escherichia coli is a member of a large family of Na+/substrate symporters. Previous work on PutP suggests an involvement of the region ranging from Asp-55 to Gly-58 in binding of Na+ and/or proline (Pirch, T., Quick, M., N... |
|
|
Mapping out regions on the surface of the aspartate receptor that are essential for kinase activation.
Biochemistry 42(10) , 2952-9, (2003) The aspartate receptor of bacterial chemotaxis is representative of a large family of taxis receptors widespread in prokaryotes. The homodimeric receptor associates with cytoplasmic components to form a receptor-kinase signaling complex. Within this complex t... |
|
|
Function of transmembrane domain IX in the Na+/proline transporter PutP.
J. Mol. Biol. 382(4) , 884-93, (2008) Selected residues of transmembrane domain (TM) IX were previously shown to play key roles in ligand binding and transport in members of the Na(+)/solute symporter family. Using the Na(+)/proline transporter PutP as a model, a complete Cys scanning mutagenesis... |