Ryanodine
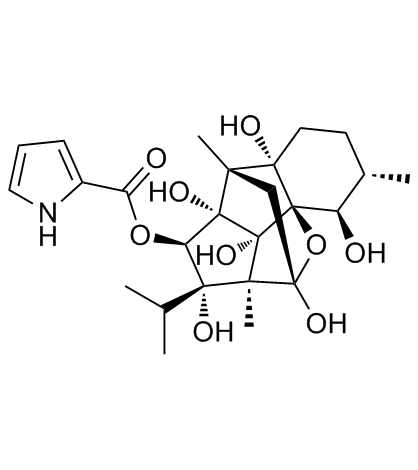
Ryanodine structure
|
Common Name | Ryanodine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 15662-33-6 | Molecular Weight | 493.547 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 714.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H35NO9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 385.7±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Physiologic force-frequency response in engineered heart muscle by electromechanical stimulation.
Biomaterials 60 , 82-91, (2015) A hallmark of mature mammalian ventricular myocardium is a positive force-frequency relationship (FFR). Despite evidence of organotypic structural and molecular maturation, a positive FFR has not been observed in mammalian tissue engineered heart muscle. We h... |
|
|
Ammonium increases Ca(2+) signalling and upregulates expression of Cav1.2 gene in astrocytes in primary cultures and in the in vivo brain.
Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 214 , 261-74, (2015) The primary aim of this study was to identify the effects of hyperammonaemia on functional expression of Cav1.2 L-type Ca(2+) channels in astroglia.Primary cultures of mouse astrocytes were used to study effects of chronic treatment (1-5 days) with ammonium c... |
|
|
Effects of caffeine on circadian phase, amplitude and period evaluated in cells in vitro and peripheral organs in vivo in PER2::LUCIFERASE mice.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 171(24) , 5858-69, (2014) Caffeine is one of the most commonly used psychoactive substances. Circadian rhythms consist of the main suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) clocks and peripheral clocks. Although caffeine lengthens circadian rhythms and modifies phase changes in SCN-operated rhyth... |
|
|
Mechanisms of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release induced by P2X receptor activation in mesenteric artery myocytes.
Pharmacol. Rep. 66(3) , 363-72, (2014) ATP is one of the principal sympathetic neurotransmitters which contracts vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) via activation of ionotropic P2X receptors (P2XRs). We have recently demonstrated that contraction of the guinea pig small mesenteric arteries evoked... |
|
|
Effects of fluvastatin and coenzyme Q10 on skeletal muscle in normo- and hypercholesterolaemic rats.
J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 36 , 263-74, (2015) Myalgia and muscle weakness may appreciably contribute to the poor adherence to statin therapy. Although the pathomechanism of statin-induced myopathy is not completely understood, changes in calcium homeostasis and reduced coenzyme Q10 levels are hypothesize... |
|
|
Muscle dysfunction associated with adjuvant-induced arthritis is prevented by antioxidant treatment.
Skelet. Muscle 5 , 20, (2015) In addition to the primary symptoms arising from inflamed joints, muscle weakness is prominent and frequent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here, we investigated the mechanisms of arthritis-induced muscle dysfunction in rats with adjuvant-induced ... |
|
|
How Does the Ca(2+)-paradox Injury Induce Contracture in the Heart?-A Combined Study of the Intracellular Ca(2+) Dynamics and Cell Structures in Perfused Rat Hearts.
Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 48 , 1-8, (2015) The calcium (Ca(2+))-paradox injury of the heart, induced by restoration of extracellular Ca(2+) after its short-term depletion, is known to provoke cardiomyocyte contracture. However, undetermined is how the Ca(2+)-paradox provokes such a distinctive present... |
|
|
Elevated Ca2+ transients and increased myofibrillar power generation cause cardiac hypercontractility in a model of Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308 , H1086-95, (2015) Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML) is primarily caused by mutations in the nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 and associated with congenital heart disease in the form of pulmonary valve stenosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). O... |
|
|
Disruption of Ah Receptor Signaling during Mouse Development Leads to Abnormal Cardiac Structure and Function in the Adult.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0142440, (2015) The Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD) Theory proposes that the environment encountered during fetal life and infancy permanently shapes tissue physiology and homeostasis such that damage resulting from maternal stress, poor nutrition or expo... |
|
|
A CASQ1 founder mutation in three Italian families with protein aggregate myopathy and hyperCKaemia.
J. Med. Genet. 52 , 617-26, (2015) Protein aggregate myopathies are increasingly recognised conditions characterised by a surplus of endogenous proteins. The molecular and mutational background for many protein aggregate myopathies has been clarified with the discovery of several underlying mu... |