Cantharidin
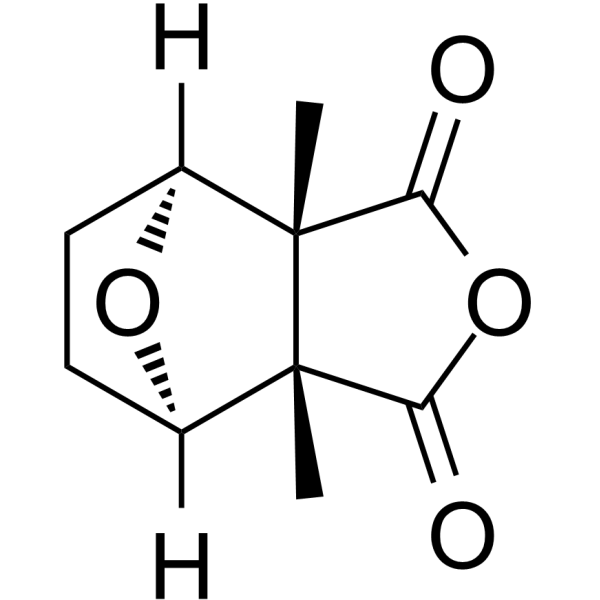
Cantharidin structure
|
Common Name | Cantharidin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-25-7 | Molecular Weight | 196.200 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 326.9±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O4 | Melting Point | 215-217 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 146.1±26.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Crosstalk between PI3K and Ras pathways via protein phosphatase 2A in human ovarian clear cell carcinoma.
Cancer Biol. Ther. 16(2) , 325-35, (2015) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is one of the most promising pharmacological targets for all types of cancer, including ovarian cancer. Ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) has poor prognosis because of its insensitivity to chemotherapy. To elucidate the ch... |
|
|
Cantharidin represses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through accelerated degradation of MMP2 mRNA.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 11836, (2015) Cantharidin is an active constituent of mylabris, a traditional Chinese medicine, and is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) that plays an important role in cell cycle control, apoptosis, and cell-fate determination. In the prese... |
|
|
PKA reduces the rat and human KCa3.1 current, CaM binding, and Ca2+ signaling, which requires Ser332/334 in the CaM-binding C terminus.
J. Neurosci. 34(40) , 13371-83, (2014) The Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) channel, KCa3.1 (KCNN4/IK/SK4), is widely expressed and contributes to cell functions that include volume regulation, migration, membrane potential, and excitability. KCa3.1 is now considered a therapeutic target for several diseases... |
|
|
A novel cantharidin analogN-Benzylcantharidinamide reduces the expression of MMP-9 and invasive potentials of Hep3B via inhibiting cytosolic translocation of HuR
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 447(2) , 371-7, (2014) Graphical abstract |
|
|
Cantharidin induces DNA damage and inhibits DNA repair-associated protein levels in NCI-H460 human lung cancer cells.
Environ. Toxicol. 30 , 1135-43, (2015) Cantharidin is one of the major compounds from mylabris and it has cytotoxic effects in many different types of human cancer cells. Previously, we found that cantharidin induced cell death through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in human lung cancer... |
|
|
PP2A inhibitors arrest G2/M transition through JNK/Sp1- dependent down-regulation of CDK1 and autophagy-dependent up-regulation of p21.
Oncotarget 6 , 18469-83, (2015) Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) plays an important role in the control of the cell cycle. We previously reported that the PP2A inhibitors, cantharidin and okadaic acid (OA), efficiently repressed the growth of cancer cells. In the present study, we found that P... |
|
|
Endothelial progenitor cells proliferated via MEK-dependent p42 MAPK signaling pathway.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 400(1-2) , 201-6, (2015) Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) clinical applications have been well reported. However, due to low number of EPCs that could be isolated, EPCs expansion study became one of the main focuses. Some optimized mediums to culture EPCs were currently available.... |
|
|
Dephosphorylation and inactivation of NPR2 guanylyl cyclase in granulosa cells contributes to the LH-induced decrease in cGMP that causes resumption of meiosis in rat oocytes.
Development 141(18) , 3594-604, (2014) In mammals, the meiotic cell cycle of oocytes starts during embryogenesis and then pauses. Much later, in preparation for fertilization, oocytes within preovulatory follicles resume meiosis in response to luteinizing hormone (LH). Before LH stimulation, the a... |