(-)-Cholesteryl acetate
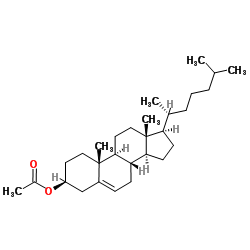
(-)-Cholesteryl acetate structure
|
Common Name | (-)-Cholesteryl acetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 604-35-3 | Molecular Weight | 428.690 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 493.3±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H48O2 | Melting Point | 112-114 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 248.8±10.4 °C | |
|
Theoretical and vibrational spectroscopic analysis of the CO stretching mode of cholesteryl alkanoates: the particular case of the cholesteryl acetate.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 62(1-3) , 547-51, (2005) Structural and vibrational properties of the CO stretching bond of cholesteryl acetate and related steroids are investigated theoretically and by Micro-Raman spectroscopy. In this work, an analysis of the CO stretching mode for the cholesteryl acetate is pres... |
|
|
Use of an improved internal-standard method in the quantitative sterol analyses of phytoplankton and oysters.
Lipids 32(9) , 1011-4, (1997) Most work reporting the sterol composition of living organisms has not been done quantitatively, although good quantitative data are available for fatty acids and many other cellular components using an internal-standard method that compensates for errors dur... |
|
|
Identification of thermal oxidation products of cholesteryl acetate.
J. Chromatogr. A. 683(1) , 75-85, (1994) The polar products separated by solid-phase extraction from the peroxidation mixture of cholesteryl acetate, were investigated. The oxidation products were identified by comparing GC retention times as well as the mass spectra against those of available or sy... |
|
|
Central leptin regulates total ceramide content and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1C proteolytic maturation in rat white adipose tissue.
Endocrinology 150(1) , 169-78, (2009) Obesity and type 2 diabetes are associated with insulin and leptin resistance, and increased ceramide contents in target tissues. Because the adipose tissue has become a central focus in these diseases, and leptin-induced increases in insulin sensitivity may ... |
|
|
Simultaneous false-colour imaging of birefringence, extinction and transmittance at camera speed.
J. Microsc. 228(Pt 2) , 153-64, (2007) A polarized light imaging technique is introduced that simultaneously captures and unfolds transmittance, fast/slow axes directions and birefringence or linear dichroism from single camera exposures. The technique, based on the rotating polarizer method, is c... |
|
|
Mass spectral fragmentations of cholesterol acetate oxidation products.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 14(14) , 1275-9, (2000) In this work, electron-impact mass spectroscopy (EI-MS) was employed on a wide range of sterol compounds in order to study their behaviour with regard to their functional groups. In particular, some specific mechanisms of fragmentation occurring in these subs... |
|
|
High performance reversed phase chromatography of cholesterol and cholesteryl esters of human plasma lipoproteins.
Lipids 16(8) , 609-13, (1981) Cholesterol and cholesteryl esters were separated according to their carbon number and number of double bonds by high performance reversed-phase chromatography (HPRC) using acetonitrile/chloroform/methanol (1:1:1, v/v) as a mobile phase. It was found that wit... |
|
|
The lipids of chalazia.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 29(3) , 482-6, (1988) The tissue contents of chalazia taken from five individuals were extracted for lipids and analyzed by TLC and GLC. Lipids found were sterol esters 9%, wax esters 0%, triacyl glycerols 4%, free cholesterol 11%, free fatty acids 2%, unidentified nonpolar materi... |
|
|
Deconvolution of complex NMR spectra in small molecules by multi frequency homonuclear decoupling (MDEC).
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(44) , 15994-5, (2009) A new technique to deconvolute complex (1)H NMR spectra of small molecules has been developed that utilizes shape selective pulses to simultaneously decouple multiple protons. A limitation in the assignment of the relative configuration of small molecules is ... |
|
|
Hepatic lipid profiling of deer mice fed ethanol using ¹H and ³¹P NMR spectroscopy: a dose-dependent subchronic study.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 264(3) , 361-9, (2012) Chronic alcohol abuse is a 2nd major cause of liver disease resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is characterized by a wide spectrum of pathologies starting from fat accumulation (steatosis) in early reversible stage... |