Myricetin
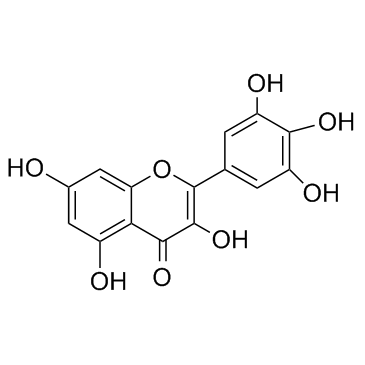
Myricetin structure
|
Common Name | Myricetin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 529-44-2 | Molecular Weight | 318.235 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 747.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O8 | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 285.9±26.4 °C | |
|
Effect of different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition and sensory characteristics of Syrah red wines fermented using different yeast strains.
Food Chem. 179 , 116-26, (2015) The effect of high levels of the polysaccharide Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strain (HPS) and another conventional yeast strain (FERM) on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition of Syrah red wines during alcoholic fermentation and subsequent aging on le... |
|
|
Effect of selected Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains and different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and polyphenolic composition and sensorial characteristics of Cabernet Sauvignon red wines.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2132-44, (2015) The objective of this work was to study the effect of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains with different capabilities of polysaccharide liberation during alcoholic fermentation in addition to subsequent aging on lees with or without oak wood chips as w... |
|
|
Rapid method for the simultaneous determination of flavonol aglycones in food using u-HPLC coupled with heating block acidic hydrolysis.
J. AOAC Int. 96(5) , 1059-64, (2013) A rapid method for the simultaneous determination of flavonol aglycones in food using ultra-high-performance LC (u-HPLC) coupled with a heating-block acidic hydrolysis method was validated in terms of precision, accuracy, and linearity. The u-HPLC separation ... |
|
|
Novel insight into qualitative standardization of Polygoni avicularis herba (Ph. Eur.).
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 72 , 216-22, (2013) Polygonum aviculare L. (Common Knotrgrass) (Polygonaceae Juss.) is an annual from which pharmacopoeial (Ph. Eur.) plant material Polygoni avicularis herba is obtained. Although its main active constituents are flavonoids and its standardization is based on th... |
|
|
Effects of UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic composition of leaves and berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Graciano.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(2) , 409-16, (2014) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces adaptive responses that can be used for plant production improvement. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of solar UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic compounds of leaves and berry skins of Vitis vinifera ... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Analysis of different European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars: authentication, phenotypic features, and phenolic profiles.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(26) , 6236-46, (2014) Hazelnuts exhibit functional properties due to their content in fatty acids and phenolic compounds that could positively affect human health. The food industry requires precise traits for morphological, chemical, and physical kernel features so that some cult... |
|
|
Comparative Studies on Polyphenolic Composition, Antioxidant and Diuretic Effects of Nigella sativa L. (Black Cumin) and Nigella damascena L. (Lady-in-a-Mist) Seeds.
Molecules 20 , 9560-74, (2015) This study was performed to evaluate the phenolic profile, antioxidant and diuretic effects of black cumin and lady-in-a-mist seeds. In the phenolic profile, differences between the two species are significant. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of the phe... |
|
|
Investigating the potential of under-utilised plants from the Asteraceae family as a source of natural antimicrobial and antioxidant extracts.
Food Chem. 161 , 79-86, (2014) Antimicrobial properties of ethanol and water extracts from eight Asteraceae species were investigated against three Gram positive (Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and Bacillus cereus) and two Gram negative (Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium) bacterial ... |
|
|
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of phenolic constituents in honey from various floral sources using multiwalled carbon nanotubes as extraction sorbents.
J. Sep. Sci. 38 , 2597-606, (2015) An ultra high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry method has been developed for the simultaneous separation, identification and determination of 22 phenolic constituents in honey from various floral sources from Yemen. Solid-phase extract... |