Chondroitin sulfate A sodium salt
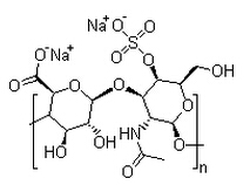
Chondroitin sulfate A sodium salt structure
|
Common Name | Chondroitin sulfate A sodium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39455-18-0 | Molecular Weight | 515.37638 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | (C14H19NO14SNa2)n | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
In vitro reconstitution of complexes between pro-matrix metalloproteinase-9 and the proteoglycans serglycin and versican.
FEBS J. 280(12) , 2870-87, (2013) Previously, we have shown that a proportion of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) synthesized by the macrophage cell line THP-1 binds to a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG) core protein to form a reduction-sensitive heteromer. It was also shown that... |
|
|
Efficacy and safety of antifungal additives in Optisol-GS corneal storage medium.
JAMA Ophthalmol. 132(7) , 832-7, (2014) Optisol-GS, the most common corneal storage medium in the United States, contains antibacterial but no antifungal supplementation. Most postkeratoplasty endophthalmitis and keratitis cases are now of a fungal origin.To assess the efficacy and safety of vorico... |
|
|
Chondroitin Sulfate is the Primary Receptor for a Peptide-Modified AAV That Targets Brain Vascular Endothelium In Vivo.
Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 3 , e202, (2014) Recently, we described a peptide-modified AAV2 vector (AAV-GMN) containing a capsid-displayed peptide that directs in vivo brain vascular targeting and transduction when delivered intravenously. In this study, we sought to identify the receptor that mediates ... |
|
|
Trypan blue vital dye staining vs TUNEL technique to detect corneal endothelium toxic effects.
JAMA Ophthalmol. 132(12) , 1491, (2014)
|
|
|
Anti-oxidation and Antiapoptotic Effects of Chondroitin Sulfate on 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Injury Through the Up-Regulation of Nrf2 and Inhibition of Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway.
Neurochem. Res. 40 , 1509-19, (2015) The purpose of the study was to investigate the protective effect and molecular mechanism of chondroitin sulfate (CS) against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induced toxicity in the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. The results showed that CS could protect SH... |
|
|
Solute transport across the articular surface of injured cartilage.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 535(2) , 241-7, (2013) Solute transport through extracellular matrix (ECM) is important to physiology and contrast agent-based clinical imaging of articular cartilage. Mechanical injury is likely to have important effects on solute transport since it involves alteration of ECM stru... |
|
|
Hyaluronic acid decreases IL-6 and IL-8 secretion and permeability in an inflammatory model of interstitial cystitis.
Acta Biomater. 19 , 66-75, (2015) Hyaluronic acid (HA) has received a lot of attention recently as a biomaterial with applications in wound healing, drug delivery, vascular repair and cell and/or gene delivery. Interstitial cystitis (IC) is characterised by an increase in the permeability of ... |
|
|
Effect of hydration state and storage media on corneal biomechanical response from in vitro inflation tests.
J. Refract. Surg. 29(7) , 490-7, (2013) To evaluate corneal deformation with varying intraocular pressure and the dependency of the biomechanical response on the corneal hydration state, modulated by the storage solutions or postmortem period.Thirty fresh enucleated porcine eyes were used for in vi... |
|
|
Melamine nanosensing with chondroitin sulfate-reduced gold nanoparticles.
J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13(12) , 8229-38, (2013) Gold nanoparticles were green-synthesized using a glycosaminoglycan, chondroitin sulfate, as the reducing agent by mixing Au3+ and chondroitin sulfate under heating. Chondroitin sulfate-reduced gold nanoparticles were characterized by UV-Vis spectrophotometry... |
|
|
Influence of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid presence in nanofibers and its alignment on the bone marrow stromal cells: cartilage regeneration.
J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 10(8) , 1469-79, (2014) Cartilage degeneration is the major cause of disability and poses several challenges to repair and regenerate. Conventional surgical treatments often induce fibrous tissues and compromise its function. Alternative tissue engineering strategies utilized scaffo... |