Dithiobiuret
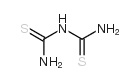
Dithiobiuret structure
|
Common Name | Dithiobiuret | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 541-53-7 | Molecular Weight | 135.21100 | |
| Density | 1.541g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 272.1ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5N3S2 | Melting Point | 181 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 118.3ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Temporal analysis of dithiobiuret neurotoxicity in rats and assessment of potential nonneural causes.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 91(2) , 212-21, (1987) To evaluate the hypothesis that depressed neuromuscular transmission causes dithiobiuret (DTB)-induced muscle weakness in rats, the temporal development of impaired treadmill performance and deficits in the nerve-elicited muscle contractions were compared dur... |
|
|
Voltage clamp analysis reveals multiple populations of quanta released at neuromuscular junctions of rats treated with 2,4-dithiobiuret.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256(1) , 159-63, (1991) Rats treated with small daily doses of 2,4-dithiobiuret (DTB) develop a delayed onset neuromuscular weakness after 4-6 days of treatment. Analysis of quantal release using nerve-muscle preparations taken from rats exhibiting neuromuscular weakness demonstrate... |
|
|
Differential effects of 2,4-dithiobiuret on the synthesis and release of acetylcholine and dopamine from rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275(3) , 1453-62, (1995) Chronic administration of 2,4-dithiobiuret (DTB), causes delayed-onset neuromuscular weakness in rats. This effect results from inhibition of quantal release of acetylcholine (ACh) from motor nerve terminals. The effects of noncholinergic neurotransmission ar... |
|
|
Morphometric characterization of the neuromuscular junction of rodents intoxicated with 2,4-dithiobiuret: evidence that nerve terminal recycling processes contribute to muscle weakness.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 196(2) , 266-86, (2004) 2,4-Dithiobiuret (DTB) causes ascending motor weakness when given chronically to rodents. In muscles of animals with DTB-induced weakness, quantal release of acetylcholine (ACh) is impaired. We examined in detail the structural changes that occurred at neurom... |
|
|
2,4-Dithiobiuret in rats: cognitive facilitation after acute injection precedes motor impairment after repeated daily injections.
Psychopharmacology 123(3) , 267-79, (1996) 2,4-Dithiobiuret (DTB) is a sulfonated derivative of urea that is used as a reducing agent in chemical manufacture. Its low acute toxicity to rodents belies a peripherally mediated, delayed-onset muscle weakness which develops during repeated daily exposure. ... |
|
|
Impairment of synaptic vesicle exocytosis and recycling during neuromuscular weakness produced in mice by 2,4-dithiobiuret.
J. Neurophysiol. 88(6) , 3243-58, (2002) Chronic treatment of rodents with 2,4-dithiobiuret (DTB) induces a neuromuscular syndrome of flaccid muscle weakness that mimics signs seen in several human neuromuscular disorders such as congenital myasthenic syndromes, botulism, and neuroaxonal dystrophy. ... |
|
|
Excretion of porphyrins and porphyrin precursors during neuromuscular paralysis produced by dithiobiuret.
Exp. Neurol. 85(1) , 63-8, (1984) Urinary excretion of porphyrin precursors delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG) and total porphyrins was measured during intoxication of rats with 2,4-dithiobiuret (DTB), a chemical which produces delayed-onset neuromuscular weakness, in a... |
|
|
High dose refractoriness to the neuromuscular toxicity of dithiobiuret in rats.
Neurotoxicology 13(2) , 331-45, (1992) Increasing the daily dose of dithiobiuret (DTB) given to rats from 0.5 to 1 to 5 mg/kg shortened the latency to onset of treadmill failure and associated flaccid muscle tone from 7 to 5 to 3 days, respectively. Death generally did not follow treadmill failure... |
|
|
Effects of dithiobiuret intoxication on motor end plates in sternocostalis and hindlimb muscles of female rats.
Acta Neuropathol. 65(1) , 77-84, (1984) Daily dosing with 1-3 mg/kg dithiobiuret for 4-5 days causes progressive, generalised muscle weakness which is fatal in about 50% of cases on day 4 or 5. Survivors recover mobility by day 7 and appear normal, although still weak. Striking changes in the motor... |
|
|
Glucose-dependent lactate production by homogenates of neuronal tissues prepared from rats treated with 2,4-dithiobiuret, acrylamide, p-bromophenylacetylurea and 2,5-hexanedione.
Neurotoxicology 5(2) , 25-35, (1984) Chronic treatment of rats with dithiobiuret (DTB) produces a delayed onset muscle weakness and, as suggested by a preliminary study, a distal axonopathy. An inhibition of glycolysis resulting in an energy deficit has been suggested as a possible mechanism of ... |