NS309
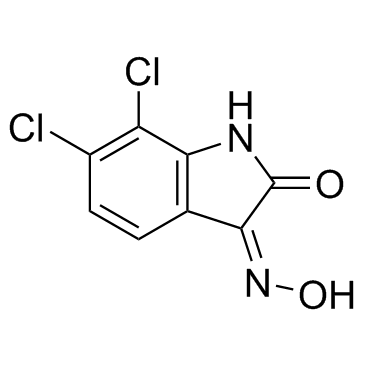
NS309 structure
|
Common Name | NS309 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 18711-16-5 | Molecular Weight | 231.036 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H4Cl2N2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Inactivation of Endothelial Small/Intermediate Conductance of Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels Contributes to Coronary Arteriolar Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients.
J. Am. Heart Assoc. 4 , e002062, (2015) Diabetes is associated with coronary arteriolar endothelial dysfunction. We investigated the role of the small/intermediate (SK(Ca)/IK(Ca)) conductance of calcium-activated potassium channels in diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction.Coronary arterioles (80... |
|
|
Duration differences of corticostriatal responses in striatal projection neurons depend on calcium activated potassium currents.
Front. Syst. Neurosci. 7 , 63, (2013) The firing of striatal projection neurons (SPNs) exhibits afterhyperpolarizing potentials (AHPs) that determine discharge frequency. They are in part generated by Ca(2+)-activated K(+)-currents involving BK and SK components. It has previously been shown that... |
|
|
Stimulation of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels inhibits neurogenic contraction of human bladder from patients with urinary symptoms and reverses acetic acid-induced bladder hyperactivity in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 735 , 68-76, (2014) We have analysed the effects of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel (BK) stimulation on neurogenic and myogenic contraction of human bladder from healthy subjects and patients with urinary symptoms and evaluated the efficacy of activating BK... |
|
|
Jensen, B.S., et al.
Abstr. Soc. Neurosci 2003 , 367.19
|
|
|
Pedarzani, P., et al.
Abstr. Soc. Neurosci , 367.20, (2003)
|
|
|
The SK3 channel promotes placental vascularization by enhancing secretion of angiogenic factors.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 307(10) , E935-43, (2014) Proper placental perfusion is essential for fetal exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste with the maternal circulation. Impairment of uteroplacental vascular function can lead to pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restri... |
|
|
Daily variation in the electrophysiological activity of mouse medial habenula neurones.
J. Physiol. 592 , 587-603, (2014) Intrinsic daily or circadian rhythms arise through the outputs of the master circadian clock in the brain's suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) as well as circadian oscillators in other brain sites and peripheral tissues. SCN neurones contain an intracellular molecu... |