SC-58125
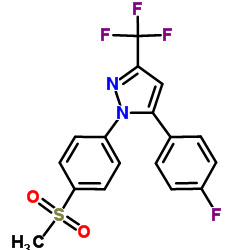
SC-58125 structure
|
Common Name | SC-58125 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 162054-19-5 | Molecular Weight | 384.348 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 512.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H12F4N2O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 263.8±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
The dual role of prostaglandin E(2) in excitotoxicity and preconditioning-induced neuroprotection.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 517(1-2) , 17-27, (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2 is harmful in models of cerebral ischemia yet plays a protective role in preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance in the heart. This study examined the mechanisms underlying cyclooxygenase-2-mediated neurotoxicity and preconditioning-induce... |
|
|
CpG oligodeoxynucleotides induce cyclooxygenase-2 in human B lymphocytes: implications for adjuvant activity and antibody production.
Clin. Immunol. 125(2) , 138-48, (2007) Synthetic CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN), similar to DNA sequences found in certain microorganisms, have shown promise as adjuvants for humans by enhancing immune responses. Since antibodies are often indicators of successful vaccination, it is important to ... |
|
|
Cyclooxygenase-2 activity contributes to neuronal expression of cyclin D1 after anoxia/ischemia in vitro and in vivo.
Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 132(1) , 31-7, (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) activity has been implicated in the pathogenesis of neuronal cell death in ischemia and other diseases, but the mechanism by which COX-2 exacerbates cell death is unknown. COX-2 activity is known to induce expression of cyclin D1 in n... |
|
|
Constitutive and activation-inducible cyclooxygenase-2 expression enhances survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells.
Clin. Immunol. 120(1) , 76-90, (2006) We recently reported that activated normal human B lymphocytes express Cox-2. These findings prompted us to evaluate whether human B-CLL cells express Cox-2 and synthesize prostaglandins. In contrast to naive human B cells, B-CLL cells constitutively expresse... |
|
|
The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs protect mouse cochlea against acoustic injury.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 216(1) , 53-9, (2008) Acoustic injury is a common cause of hearing loss for people in industrial societies. Cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX) are two important enzymes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism. Two COX isozymes are characterized, COX-1 and COX-2, that diff... |
|
|
Gastric and small bowel ileus after severe burn in rats: the effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors.
Burns 35(8) , 1180-4, (2009) Gastrointestinal (GI) ileus is a common complication after severe burns. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2i) improved post-operative ileus, but its effect on burn-induced GI dysmotility is unknown. Our aim was to test whether a COX-2i improves gast... |
|
|
The cyclooxygenase inhibitor indomethacin modulates gene expression and represses the extracellular matrix protein laminin gamma1 in human glioblastoma cells.
Exp. Cell Res. 302(2) , 244-52, (2005) The induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression is associated with more aggressive gliomas and poor survival. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit COX activity and have antitumorigenic properties. In this report, our initial aim was to d... |
|
|
Cyclooxygenase isozymes are expressed in human myeloma cells but not involved in anti-proliferative effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitors.
Mol. Carcinog. 45(4) , 250-9, (2006) Considering possible tumorigenic activity of cyclooxygenase (COX) isozymes in myeloma, we examined expression levels of COX-1 and -2 in seven human myeloma cell lines (ARH-77, IM-9, RPMI-8226, HPC, HS-Sultan, TSPC-1, and U-266). As analyzed by reverse transcr... |
|
|
Ibuprofen and other widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit antibody production in human cells.
Cell. Immunol. 258(1) , 18-28, (2009) The widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) function mainly through inhibition of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 (Cox-1 and Cox-2). Unlike Cox-1, Cox-2 is considered an inducible and pro-inflammatory enzyme. We previously reported that Cox-2 is up... |
|
|
Decreased susceptibility to renovascular hypertension in mice lacking the prostaglandin I2 receptor IP.
J. Clin. Invest. 114(6) , 805-12, (2004) Persistent reduction of renal perfusion pressure induces renovascular hypertension by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; however, the sensing mechanism remains elusive. Here we investigated the role of PGI2 in renovascular hypertension in vi... |