NU7026
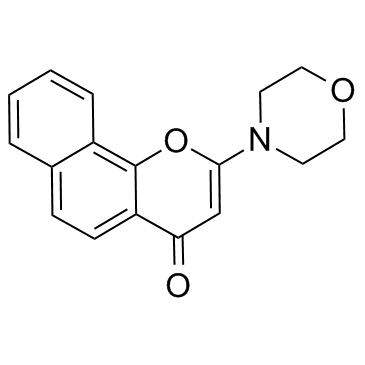
NU7026 structure
|
Common Name | NU7026 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 154447-35-5 | Molecular Weight | 281.306 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 459.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H15NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 231.9±28.7 °C | |
|
DNA double-strand breaks by Cr(VI) are targeted to euchromatin and cause ATR-dependent phosphorylation of histone H2AX and its ubiquitination.
Toxicol. Sci. 143(1) , 54-63, (2014) Hexavalent chromium is a human respiratory carcinogen that undergoes intracellular activation in vivo primarily via reduction with ascorbate. Replication of Cr-adducted DNA triggers mismatch repair that generates toxic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) as secon... |
|
|
Effects of topoisomerase inhibitors that induce DNA damage response on glucose metabolism and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in multiple myeloma cells.
Am. J. Cancer Res. 5 , 1649-64, (2015) Hallmarks of cancer cells comprise altered glucose metabolism (aerobic glycolysis) and differences in DNA damage response (DDR). Glucose transporters (GLUT), glycolytic enzymes such as hexokinase (HK) and metabolic pathways (e.g. PI3K/Akt/mTor) have been show... |
|
|
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit inhibitor reverses acquired radioresistance in lung adenocarcinoma by suppressing DNA repair.
Mol. Med. Report. 12 , 1328-34, (2015) The mechanisms underlying lung cancer radioresistance remain to be fully elucidated. The DNA repair pathway is a predominant target of radiotherapy, which is considered to be involved in the acquired radioresistance of cancer cells. The present study aimed to... |
|
|
Radiosensitizing activity of a novel Benzoxazine through the promotion of apoptosis and inhibition of DNA repair.
Invest. New Drugs 32(3) , 424-35, (2014) The DNA dependant protein kinase (DNA-PK) enzyme plays a major part in the repair of double stranded breaks induced by radiation and hence in the radio-resistance of tumour cells. Inhibitors of DNA-PK have been tested successfully in the past for their abilit... |
|
|
Role of the splicing factor SRSF4 in cisplatin-induced modifications of pre-mRNA splicing and apoptosis.
BMC Cancer 15 , 227, (2015) Modification of splicing by chemotherapeutic drugs has usually been evaluated on a limited number of pre-mRNAs selected for their recognized or potential importance in cell proliferation or apoptosis. However, the pathways linking splicing alterations to the ... |
|
|
DNA-PKcs plays role in cancer metastasis through regulation of secreted proteins involved in migration and invasion.
Cell Cycle 14 , 1961-72, (2015) The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) plays a major role in DNA damage signaling and repair and is also frequently overexpressed in tumor metastasis. We used isogenic cell lines expressing different levels of DNA-PKcs to investigate th... |
|
|
Inhibition of DNA-PKcs enhances radiosensitivity and increases the levels of ATM and ATR in NSCLC cells exposed to carbon ion irradiation.
Oncol. Lett. 10 , 2856-2864, (2016) Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) exhibits radioresistance to conventional rays, due to its DNA damage repair systems. NSCLC may potentially be sensitized to radiation treatment by reducing those factors that continuously enhance the repair of damaged DNA. I... |
|
|
FUS is phosphorylated by DNA-PK and accumulates in the cytoplasm after DNA damage.
J. Neurosci. 34(23) , 7802-13, (2014) Abnormal cytoplasmic accumulation of Fused in Sarcoma (FUS) in neurons defines subtypes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). FUS is a member of the FET protein family that includes Ewing's sarcoma (EWS) and TATA... |
|
|
PNAS-4, an Early DNA Damage Response Gene, Induces S Phase Arrest and Apoptosis by Activating Checkpoint Kinases in Lung Cancer Cells.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 14927-44, (2015) PNAS-4, a novel pro-apoptotic gene, was activated during the early response to DNA damage. Our previous study has shown that PNAS-4 induces S phase arrest and apoptosis when overexpressed in A549 lung cancer cells. However, the underlying action mechanism rem... |
|
|
Interleukin-4 enhances PARP-dependent DNA repair activity in vitro.
J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 34(9) , 734-40, (2014) Eukaryotic cells possess several DNA repair mechanisms, including homologous recombination and the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) system. There are two known NHEJ systems. The major mechanism depends on the catalytic unit of DNA-dependent protein kinase (D... |