Methyl isothiocyanate
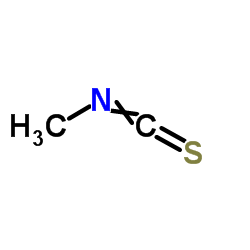
Methyl isothiocyanate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl isothiocyanate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 556-61-6 | Molecular Weight | 73.117 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 107.8±3.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3NS | Melting Point | 30-34 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 32.2±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Olfactometry Profiles and Quantitation of Volatile Sulfur Compounds of Swiss Tilsit Cheeses.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 7511-21, (2015) To establish the odor profiles of three differently fabricated commercial Swiss Tilsit cheeses, analyses were conducted using headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry/pulsed flame photometric detection and gas chromatography-... |
|
|
Human olfactory bulb neural stem cells mitigate movement disorders in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.
J. Cell Physiol. 230(7) , 1614-29, (2015) Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by the loss of midbrain dopaminergic (DA) neurons. Neural stem cells (NSCs) are multipotent stem cells that are capable of differentiating into different neuronal and glial elements. The produc... |
|
|
Absolute kinetics and reaction efficiencies of hydroxyl-radical-induced degradation of methyl isothiocyanate (MITC) in different quality waters.
Chemosphere 81(3) , 339-44, (2010) Methyl isothiocyanate (MITC), a toxic and corrosive skin and respiratory irritant, is a common soil fumigant byproduct which has become an atmospheric, aqueous, and soil contaminant. The work described here examines the degradation and potential removal of MI... |
|
|
The enantioseparation of amino acids on a teicoplanin chiral stationary phase using non-aqueous mobile phases after pre-column derivatization with sulfur-containing reagents: the considerations of mobile phase composition and analyte structure variation on resolution enhancement.
Biomed. Chromatogr. 20(8) , 718-28, (2006) Amino acids were derivatized with sulfur-containing reagents in alkaline medium and enantioresolved by HPLC on a teicoplanin chiral stationary phase. Much better resolution was achieved using methanol-based mobile phase compared with elution with acetonitrile... |
|
|
Metam sodium intoxication: the specific role of degradation products--methyl isothiocyanate and carbon disulphide--as a function of exposure.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 49(5) , 416-22, (2011) Introduction. The objective was to evaluate the toxicity of poisoning by metam sodium, a dithiocarbamate fumigant, the breakdown products of which are methyl isothiocyanate (MITC), carbon disulphide (CS2), and dihydrogen sulphide (H2S). Methods. This is a ret... |
|
|
Methyl isothiocyanate residential community air assessment for South Franklin County, Washington.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 78(1) , 19-23, (2007)
|
|
|
Illnesses related to shank application of metam-sodium, Arvin, California, July 2002.
J. Agromedicine 10(4) , 27-42, (2005) To evaluate the health effects of methyl isothiocyanate (MITC) and other byproducts resulting from the soil-incorporated (shank) application of 25,000 pounds of metam-sodium on July 8, 2002, near the community of Arvin, California.Residents in a four-block ar... |
|
|
[Determination of isothiocyanates in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography].
Se Pu 22(1) , 30-2, (2004) A reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic method (HPLC) was established for determination of isothiocyanates in human urine, which used the reaction of propyl isothiocyanate with 1,2-benzenedithiol as reference instead of the synthesis of 1,3-b... |
|
|
Physical, chemical and environmental properties of selected chemical alternatives for the pre-plant use of methyl bromide as soil fumigant.
Pest Manag. Sci. 62(2) , 99-113, (2006) Production and use of methyl bromide, a soil fumigant, are being restricted because of this chemical's deleterious effects on stratospheric ozone concentrations. Several products, some of which are currently used as soil fumigants, are being considered as pos... |
|
|
Microbial aspects of accelerated degradation of metam sodium in soil.
Phytopathology 100(4) , 367-75, (2010) Preplant soil fumigation with metam sodium is used worldwide to control soilborne diseases. The development of accelerated degradation of pesticides in soil, including metam sodium, results in reduced pesticide efficacy. Therefore, we studied microbial involv... |