N,2-Dimethylalanine
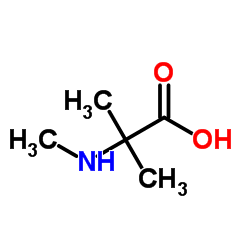
N,2-Dimethylalanine structure
|
Common Name | N,2-Dimethylalanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2566-34-9 | Molecular Weight | 117.146 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 192.5±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 | Melting Point | > 300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 70.2±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analyses of substrates of the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (hPAT1).
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 6409-18, (2011) The proton-coupled amino acid transporter hPAT1 has recently gained much interest due to its ability to transport small drugs thereby allowing their oral administration. A three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D QSAR) study has been... |
|
|
Unique antitumour effects of L-2,4 diaminobutyric acid on cultured hepatoma cells.
Anticancer Res. 23 , 1245-1248, (2003) A single hepatoma cell line was grown in vitro and incubated with L-2,4 diaminobutyric acid (DAB), a non-metabolizable amino acid, under various conditions. The tumour cells were irreversibly damaged by incubation for 8 hours with 8 mmol/L of DAB. The tumour ... |
|
|
Integrin participates in the effect of thyroxine on plasma membrane in immature rat testis.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1830(3) , 2629-37, (2013) The secretory activity of Sertoli cells (SC) is dependent on ion channel functions and protein synthesis and is critical to ongoing spermatogenesis. The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of action associated with a non-metabolizable amino aci... |
|
|
Functional activity of a large neutral amino acid transporter (LAT) in rabbit retina: a study involving the in vivo retinal uptake and vitreal pharmacokinetics of L-phenyl alanine.
Int. J. Pharm. 347(1-2) , 23-30, (2008) The purpose of this study is to elucidate the functional activity of large neutral amino acid transporter (LAT) in rabbit retina and to delineate its role in the retinal uptake and intravitreal pharmacokinetics of L-phenylalanine (L-Phe).In vivo retinal uptak... |
|
|
Transport of large neutral amino acids into BeWo cells.
Placenta 21(5-6) , 558-64, (2000) BeWo choriocarcinoma cells were cultured onto solid microcarrier beads, packed into columns and superfused. Unidirectional influx of l -phenylalanine (l -phe) and l -leucine (l -leu) across the microvillous border of the cells was studied using a rapid paired... |
|
|
Differential influence of cAMP on the expression of the three subtypes (ATA1, ATA2, and ATA3) of the amino acid transport system A.
FEBS Lett. 505(2) , 317-20, (2001) Treatment of HepG2 cells with forskolin led to 60-100% stimulation of system A activity, measured as the Na+-dependent uptake of alpha-(methylamino)isobutyric acid. The stimulation was reproducible with cholera toxin and dibutyryl cAMP, and inhibitable by H7,... |
|
|
Glutamine induces epileptiform discharges in superficial layers of the medial entorhinal cortex from pilocarpine-treated chronic epileptic rats in vitro.
Epilepsia 50(4) , 849-58, (2009) Glutamine (GLN) is a precursor for synthesis of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and has been found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) at mean concentrations of 0.6 mM. Experiments on slices are usually performed in artificial CSF (aCSF) kept free o... |
|
|
Troglitazone increases system A amino acid transport in 3T3-L1 cells.
Endocrinology 139(3) , 832-7, (1998) System A is one of the most highly regulated transport systems for transport of neutral amino acids into mammalian cells. Stimulation of uptake of alpha-[3H]methylaminoisobutyric acid (MeAIB), a nonmetabolizable system A substrate, by a novel insulin-sensitiz... |
|
|
Hypoxia inhibits amino acid uptake in human lung fibroblasts.
J. Appl. Physiol. 89(4) , 1425-31, (2000) Hypoxia and amino acid deprivation downregulate expression of extracellular matrix genes in lung fibroblasts. We examined the effect of hypoxia on amino acid uptake and protein formation in human lung fibroblasts. Low O(2) tension (0% O(2)) suppressed incorpo... |
|
|
Inhibition of hepatic stellate cell collagen synthesis by N-(methylamino)isobutyric acid.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 63(4) , 697-706, (2002) The increased deposition of extracellular matrix by hepatic stellate cells following liver injury, in a process known as activation, is considered a key mechanism for increased collagen content of liver during the development of liver fibrosis. We report that... |