Sulfabenzamide
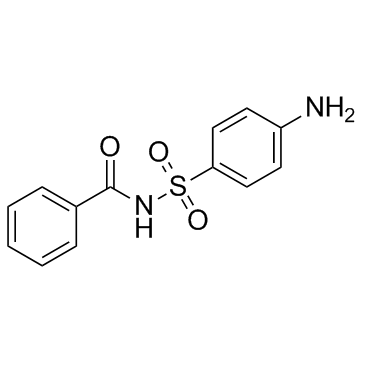
Sulfabenzamide structure
|
Common Name | Sulfabenzamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 127-71-9 | Molecular Weight | 276.311 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12N2O3S | Melting Point | 180-184 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Fast determination of 22 sulfonamides from chicken breast muscle using core-shell nanoring amino-functionalized superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted polymer followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1345 , 17-28, (2014) A novel, simple and sensitive method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 22 sulfonamides (SAs) in chicken breast muscle by using the dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction (d-μ-SPE) procedure combined with ultra-fast liquid chromatography-tan... |
|
|
In silico and in vitro filters for the fast estimation of skin permeation and distribution of new chemical entities.
J. Med. Chem. 50 , 742-8, (2007) The development of in silico and in vitro tools to estimate or predict the passive human skin permeation and distribution of new chemical entities, useful in dermal drug delivery, in absorption studies of toxic compounds, and in the cosmetics industry, is pre... |
|
|
Molecular modeling of hapten structure and relevance to broad specificity immunoassay of sulfonamide antibiotics.
Bioconjug. Chem. 10(4) , 583-8, (1999) Molecular modeling of hapten structure was used to predict and influence, through appropriate synthetic work, the outcome of an immunization program. Examination of the structures of sulfonamide antibiotics led to the development of a hypothesis and the conse... |
|
|
In vitro susceptibility of Gardnerella vaginalis and Bacteroides organisms, associated with nonspecific vaginitis, to sulfonamide preparations.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 21(6) , 870-2, (1982) Recent reports suggest that anaerobic Bacteroides organisms are frequently found with Gardnerella vaginalis in nonspecific vaginitis. Specimens taken from 96 women with vaginal discharge were tested simultaneously for these organisms. G. vaginalis was found i... |
|
|
[Physico-chemical comparison of two sulfamides: sulfaproxyline and sulfabenzamide].
Pharm. Acta Helv. 62(4) , 116-20, (1987)
|
|
|
A systematic study on hydrogen bond interactions in sulfabenzamide: DFT calculations of the N-14, O-17, and H-2 NQR parameters.
Biophys. Chem. 139(2-3) , 116-22, (2009) A systematic computational study was carried out to characterize the hydrogen bond, HB, interactions of sulfabenzamide crystal structure by DFT calculations of electric field gradient, EFG, tensors at the sites of 14N, 17O, and 2H nuclei. The computations wer... |
|
|
Electron ionization mass spectra of alkylated sulfabenzamides.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 25(6) , 750-4, (2011) Mono-, di- and trialkyl derivatives of 'sulfabenzamide' (N-4-aminophenylsulfonylbenzamide) have been prepared and their electron ionization (EI) mass spectra examined. It is found that the fragmentation of N-alkylsulfabenzamides (alkyl = CH(3) to n-C(5)H(11))... |