Electron ionization mass spectra of alkylated sulfabenzamides.
Nino G Todua, Kirill V Tretyakov, Roman S Borisov, Dmitry I Zhilyaev, Vladimir G Zaikin, Stephen E Stein, Anzor I Mikaia
Index: Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 25(6) , 750-4, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Mono-, di- and trialkyl derivatives of 'sulfabenzamide' (N-4-aminophenylsulfonylbenzamide) have been prepared and their electron ionization (EI) mass spectra examined. It is found that the fragmentation of N-alkylsulfabenzamides (alkyl = CH(3) to n-C(5)H(11)) proceeds via a very specific rearrangement process. The proposed mechanism involves an intermediate formation of distonic molecular ions, and the driving force for this process is the formation of stable N-alkylphenylcyanide cations [R-N(+)≡CC(6)H(5)]. The findings are confirmed by exact mass measurements, tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) experiments and deuterium labeling.This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the U.S.A. Published in 2011 by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
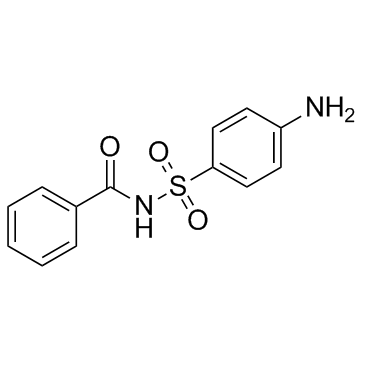 |
Sulfabenzamide
CAS:127-71-9 |
C13H12N2O3S |
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety ...
2011-12-01 [J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006)] |
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the predicti...
2010-07-19 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010)] |
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-indu...
2010-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010)] |
|
Fast determination of 22 sulfonamides from chicken breast mu...
2014-06-06 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1345 , 17-28, (2014)] |
|
In silico and in vitro filters for the fast estimation of sk...
2007-02-22 [J. Med. Chem. 50 , 742-8, (2007)] |