Lead(II) nitrate
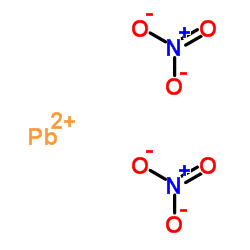
Lead(II) nitrate structure
|
Common Name | Lead(II) nitrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10099-74-8 | Molecular Weight | 331.21000 | |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C | Boiling Point | 83ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | N2O6Pb | Melting Point | 470 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |





GHS03, GHS05, GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Hepatic expression of spermatogenic genes and their transiently remarkable downregulations in Wistar-Kyoto rats in response to lead-nitrate administration: strain-difference in the gene expression patterns.
J. Toxicol. Sci. 36(3) , 357-64, (2011) Administration of lead ion (Pb) to rats and mice affects hepatic functions such as the induction of hepatic cell proliferation and upregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis. To identify the genes for which expression changes in response to Pb-administration, w... |
|
|
Protective effect of Withania somnifera roots extract on hematoserological profiles against lead nitrate-induced toxicity in mice.
Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 49(6) , 458-62, (2012) The in vivo protective role of hydro-methanolic root extract of Withania somnifera (WS) was evaluated in alleviating lead nitrate (LN)-induced toxicity in male Swiss albino mice by measuring hematoserological profiles. The lead-treated (20 mg/kg body wt, p.o.... |
|
|
Effect of lead on human erythrocytes: an in vitro study.
Acta Pol. Pharm. 68(5) , 653-6, (2011) The present study was an attempt to investigate toxic effects of lead on red blood corpuscle (RBC) under in vitro conditions. Venous blood samples from adult, healthy, well-nourished male donors falling in age group of 25-30 years were collected in EDTA vials... |
|
|
Inhibition of bacterial oxidation of ferrous iron by lead nitrate in sulfate-rich systems.
J. Hazard. Mater. 244-245 , 718-25, (2013) Inhibition of bacterial oxidation of ferrous iron (Fe(II)) by Pb(NO(3))(2) was investigated with a mixed culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. The culture was incubated at 30 °C in ferrous-sulfate medium amended with 0-24.2 mM Pb(II) added as Pb(NO(3))(2... |
|
|
Experimental aspects in acquisition of wide bandwidth solid-state MAS NMR spectra of low-γ nuclei with different opportunities on two commercial NMR spectrometers.
J. Magn. Reson. 211(2) , 195-206, (2011) The acquisition and different appearances observed for wide bandwidth solid-state MAS NMR spectra of low-γ nuclei, using (14)N as an illustrative nucleus and employing two different commercial spectrometers (Varian, 14.1T and Bruker, 19.6T), have been compare... |
|
|
Lead-induced neurodegenerative events and abnormal behaviors occur via ORXRergic/GABA(A)Rergic mechanisms in a marine teleost.
Aquat. Toxicol. 126 , 231-41, (2013) The hindering effects of metals and in particular lead (Pb) are representing a growing threat to aquatic organisms such as fish. This observation derives from toxic concentrations of Pb accounting for altered neurophysiological activities of some interesting ... |
|
|
Protective potential of Black grapes against lead induced oxidative stress in rats.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 35(3) , 361-8, (2013) From time immemorial Vitis vinifera (Black grapes) have been used both for medicinal and nourishment purposes. The aim of this study is to investigate the protective effect of Black grapes against lead nitrate induced oxidative stress. Exposure to lead signif... |
|
|
The influence of selenium on root growth and oxidative stress induced by lead in Vicia faba L. minor plants.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 147(1-3) , 320-8, (2012) The effect of selenium (Se) on Vicia faba L. minor roots subjected to lead (Pb) stress was studied by investigating root growth, root viability, and antioxidant enzyme activity. The experiments were carried out on plants grown for 2 weeks on Hoagland medium s... |
|
|
Impact of lead and mercuric ions on the interleukin-2-dependent proliferation and survival of T cells.
Arch. Toxicol. 87(2) , 249-58, (2013) Mercury and lead are widespread in the environment, causing chronic exposure of a large population to low concentrations of these metals. While several studies demonstrated that low levels of both metals affect the immune system, little is known about underly... |
|
|
A new biological test utilising the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the rapid detection of toxic substances in water.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 33(3) , 459-64, (2012) This study evaluates the toxic effects of five substances (atropine, fenitrothion, potassium cyanide, mercuric chloride and lead nitrate) on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It describes a new biological toxicity test based on inhibition of S. cerevisiae v... |