Laurdan
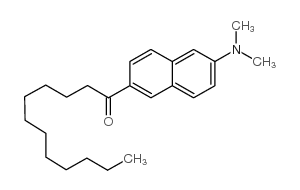
Laurdan structure
|
Common Name | Laurdan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 74515-25-6 | Molecular Weight | 353.54100 | |
| Density | 0.987g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 497.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H35NO | Melting Point | 88ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 177.4ºC | |
|
Interactions of beta-blockers with model lipid membranes: molecular view of the interaction of acebutolol, oxprenolol, and propranolol with phosphatidylcholine vesicles by time-dependent fluorescence shift and molecular dynamics simulations.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 87(3) , 559-69, (2014) Since pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic activities of drugs are often related to their interactions with biomembranes, it is of high interest to establish an approach for the characterization of these interactions at the molecular level. For the present stu... |
|
|
Deoxycholic acid modulates cell death signaling through changes in mitochondrial membrane properties.
J. Lipid Res. 56 , 2158-71, (2015) Cytotoxic bile acids, such as deoxycholic acid (DCA), are responsible for hepatocyte cell death during intrahepatic cholestasis. The mechanisms responsible for this effect are unclear, and recent studies conflict, pointing to either a modulation of plasma mem... |
|
|
Molecular mechanism of action of chlorogenic acid on erythrocyte and lipid membranes.
Mol. Membr. Biol. 32 , 46-54, (2015) The high antioxidant capacity of chlorogenic acid (CGA) in respect to biological systems is commonly known, though the molecular mechanism underlying that activity is not known. The aim of the study was to determine that mechanism at the molecular and cell le... |
|
|
ER stress induced by the OCH1 mutation triggers changes in lipid homeostasis in Kluyveromyces lactis.
Res. Microbiol. 166(2) , 84-92, (2015) In Kluyveromyces lactis yeast, OCH1 encodes for the α-1,6-mannosyltrasferase that adds the initial α-1,6-mannose to the outer-chains of N-glycoproteins. Kloch1-1 mutant cells showed altered calcium homeostasis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Since ER p... |
|
|
Slow Relaxation of Shape and Orientational Texture in Membrane Gel Domains.
Langmuir 31 , 12699-707, (2015) Gel domains in lipid bilayers are structurally more complex than fluid domains. Growth dynamics can lead to noncircular domains with a heterogeneous orientational texture. Most model membrane studies involving gel domain morphology and lateral organization as... |
|
|
Structuration in the interface of direct and reversed micelles of sucrose esters, studied by fluorescent techniques.
PLoS ONE 10(4) , e0123669, (2015) Reactors found in nature can be described as micro-heterogeneous systems, where media involved in each micro-environment can behave in a markedly different way compared with the properties of the bulk solution. The presence of water molecules in micro-organiz... |
|
|
Segregative clustering of Lo and Ld membrane microdomains induced by local pH gradients in GM1-containing giant vesicles: a lipid model for cellular polarization.
Langmuir 28(47) , 16327-37, (2012) Several cell polarization processes are coupled to local pH gradients at the membrane surface. We have investigated the involvement of a lipid-mediated effect in such coupling. The influence of lateral pH gradients along the membrane surface on lipid microdom... |
|
|
Lo/Ld phase coexistence modulation induced by GM1.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1838(8) , 2105-14, (2014) Lipid rafts are assumed to undergo biologically important size-modulations from nanorafts to microrafts. Due to the complexity of cellular membranes, model systems become important tools, especially for the investigation of the factors affecting "raft-like" L... |
|
|
Actin filaments attachment at the plasma membrane in live cells cause the formation of ordered lipid domains.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta , (2012) The relationship between ordered plasma membrane nanodomains, known as lipid rafts, and actin filaments is the focus of this study. Plasma membrane order was followed in live cells at 37°C using laurdan and di-4-ANEPPDHQ to report on lipid packing. Disrupting... |
|
|
MEK1 transduces the prion protein N2 fragment antioxidant effects.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72(8) , 1613-29, (2015) The prion protein (PrP(C)) when mis-folded is causally linked with a group of fatal neurodegenerative diseases called transmissible spongiform encephalopathies or prion diseases. PrP(C) normal function is still incompletely defined with such investigations co... |