Laurdan
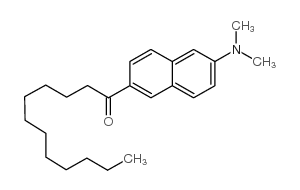
Laurdan structure
|
Common Name | Laurdan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 74515-25-6 | Molecular Weight | 353.54100 | |
| Density | 0.987g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 497.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H35NO | Melting Point | 88ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 177.4ºC | |
Use of LaurdanLaurdan is a membrane-permeable fluorescent probe that displays spectral sensitivity to the phospholipid phase of the cell membrane to which it is bound. Quantitation of generalized polarization (GP) of Laurdan can be used to identify phospholipid phase. |
| Name | 1-[6-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-2-yl]dodecan-1-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Laurdan is a membrane-permeable fluorescent probe that displays spectral sensitivity to the phospholipid phase of the cell membrane to which it is bound. Quantitation of generalized polarization (GP) of Laurdan can be used to identify phospholipid phase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 0.987g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 497.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 88ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C24H35NO |
| Molecular Weight | 353.54100 |
| Flash Point | 177.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 353.27200 |
| PSA | 20.31000 |
| LogP | 7.00940 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.553 |
| InChIKey | JHDGGIDITFLRJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)c1ccc2cc(N(C)C)ccc2c1 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Interactions of beta-blockers with model lipid membranes: molecular view of the interaction of acebutolol, oxprenolol, and propranolol with phosphatidylcholine vesicles by time-dependent fluorescence shift and molecular dynamics simulations.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 87(3) , 559-69, (2014) Since pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic activities of drugs are often related to their interactions with biomembranes, it is of high interest to establish an approach for the characterization of the... |
|
|
Deoxycholic acid modulates cell death signaling through changes in mitochondrial membrane properties.
J. Lipid Res. 56 , 2158-71, (2015) Cytotoxic bile acids, such as deoxycholic acid (DCA), are responsible for hepatocyte cell death during intrahepatic cholestasis. The mechanisms responsible for this effect are unclear, and recent stud... |
|
|
Molecular mechanism of action of chlorogenic acid on erythrocyte and lipid membranes.
Mol. Membr. Biol. 32 , 46-54, (2015) The high antioxidant capacity of chlorogenic acid (CGA) in respect to biological systems is commonly known, though the molecular mechanism underlying that activity is not known. The aim of the study w... |
| 6-Dodecanoyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-naphthylamine |
| N,N-Dimethyl-6-dodecanoyl-2-naphthylamine |
| Laurdan |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)-6-dodecanoylnaphthalene |
| 6-Dodecanoyl-2-dimethylaminonaphthalene |

